A Journey Through Europe: Understanding The Interplay Of Rivers And Mountains
A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains
Related Articles: A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains
- 3.1 Mapping the Flow: Europe’s Rivers
- 3.2 Reaching for the Sky: Europe’s Mountains
- 3.3 The Interplay of Rivers and Mountains: A Symphony of Nature
- 3.4 Understanding the Map: A Tool for Exploration
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Using a Rivers and Mountains Map
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains
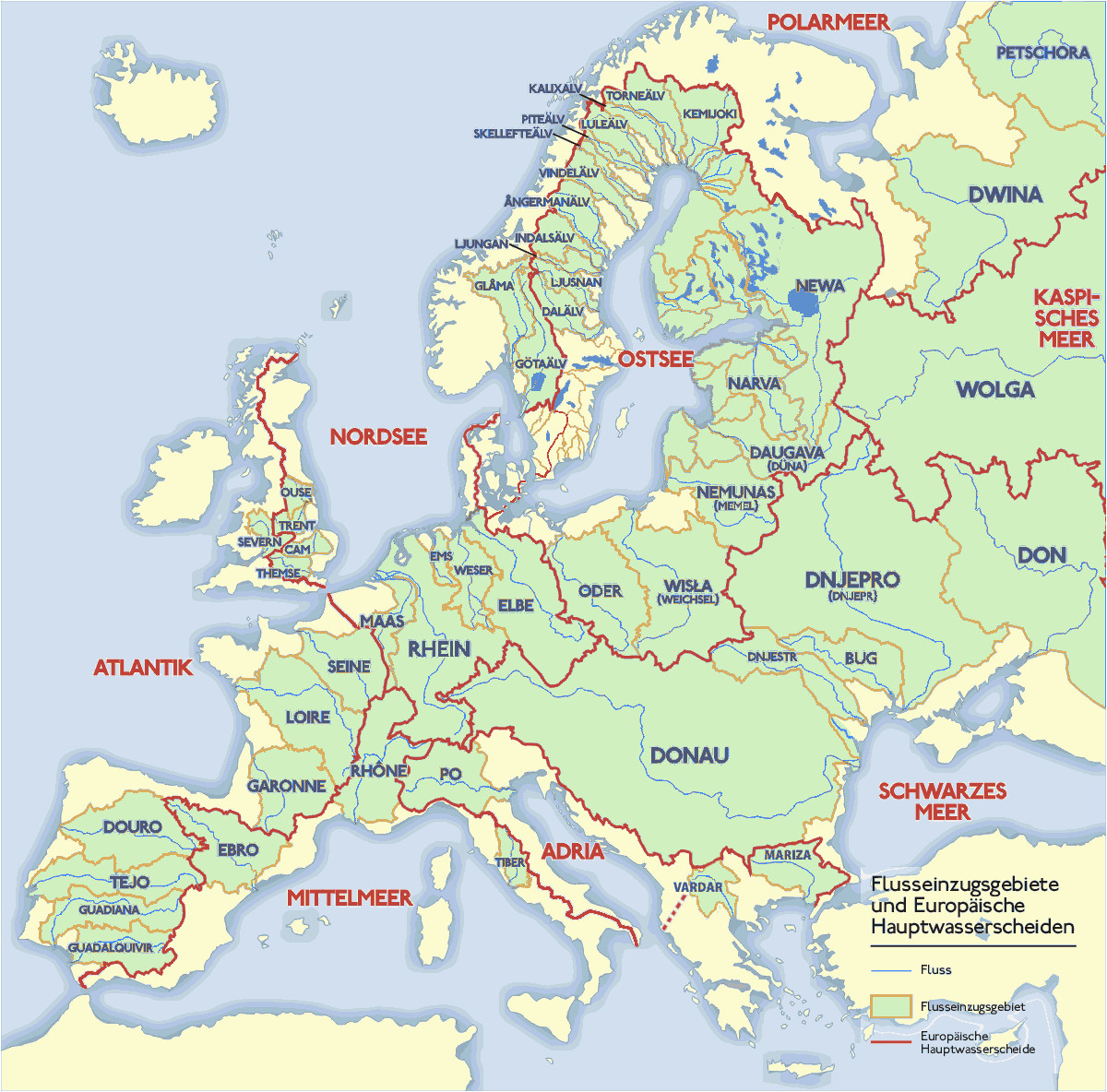
Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is intricately woven together by its vast network of rivers and imposing mountain ranges. These natural features have shaped the continent’s geography, climate, and human development for millennia. A closer examination of Europe’s rivers and mountains, through the lens of a comprehensive map, reveals a fascinating tapestry of interconnectedness and influence.
Mapping the Flow: Europe’s Rivers
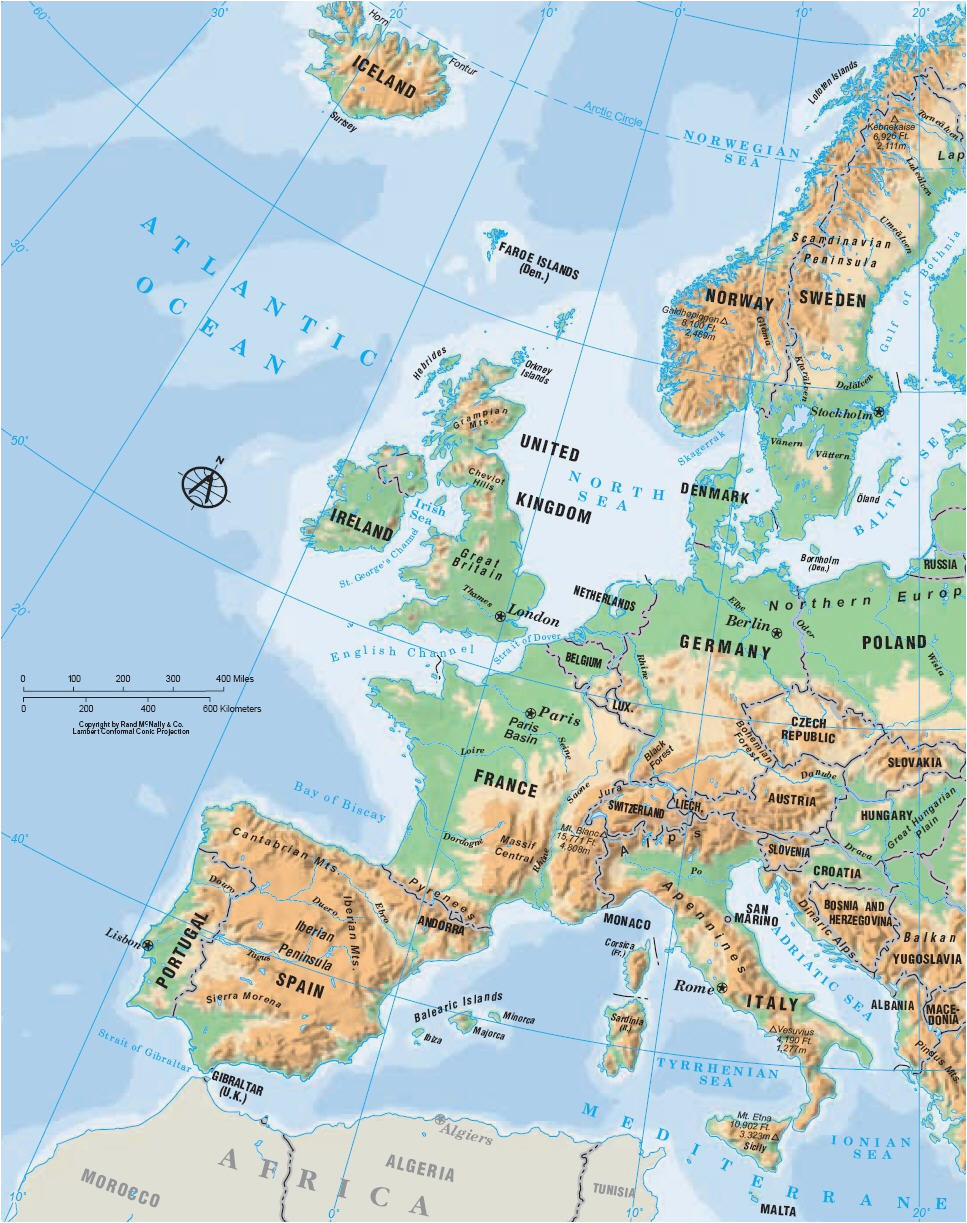
Europe’s rivers, like arteries coursing through the body, play a vital role in the continent’s lifeblood. From the mighty Danube, winding its way through ten countries, to the serene Thames, meandering through the heart of England, each river holds a unique story.
Major River Systems:
- The Danube: Europe’s second-longest river, the Danube flows for over 2,850 kilometers, traversing through ten countries, including Germany, Austria, Hungary, and Romania. It serves as a crucial waterway for trade and transportation, connecting the Black Sea to the North Sea via canals.
- The Rhine: The Rhine, originating in the Swiss Alps, flows through Germany, France, and the Netherlands, before emptying into the North Sea. It is a vital commercial artery, carrying goods and people along its course.
- The Volga: The Volga, Europe’s longest river, flows through Russia, emptying into the Caspian Sea. It is a major source of water for irrigation and hydroelectric power, and its basin is home to a significant portion of Russia’s population.
- The Elbe: The Elbe flows through Germany and the Czech Republic, before emptying into the North Sea. It is a significant waterway for shipping and is also a popular destination for recreational activities.
- The Po: The Po, Italy’s longest river, flows through the Po Valley, a fertile agricultural region. It is a vital source of water for irrigation and is also important for hydroelectric power generation.
Significance of Rivers:
- Transportation and Trade: Rivers have historically served as vital pathways for trade and transportation, connecting cities and regions. This remains true today, with many rivers serving as important commercial arteries for goods and people.
- Agriculture and Irrigation: Rivers provide water for irrigation, supporting agriculture in fertile river valleys. This is particularly important in regions with dry climates.
- Hydroelectric Power: Many rivers are harnessed for hydroelectric power generation, providing clean and renewable energy.
- Tourism and Recreation: Rivers offer opportunities for recreation, including boating, fishing, and wildlife viewing.
- Biodiversity: Rivers are home to a diverse range of plant and animal life, playing a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity.
Reaching for the Sky: Europe’s Mountains
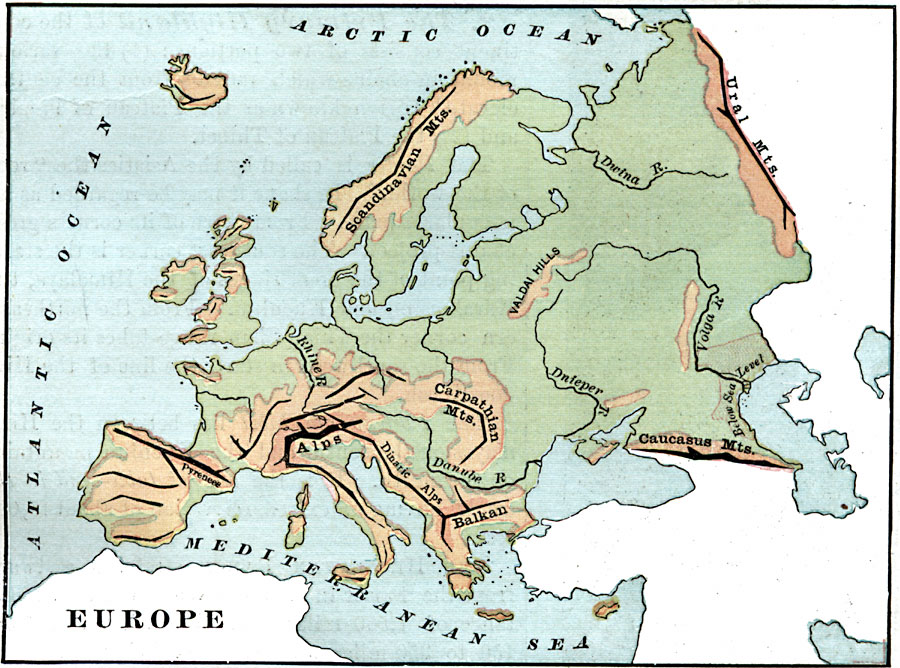
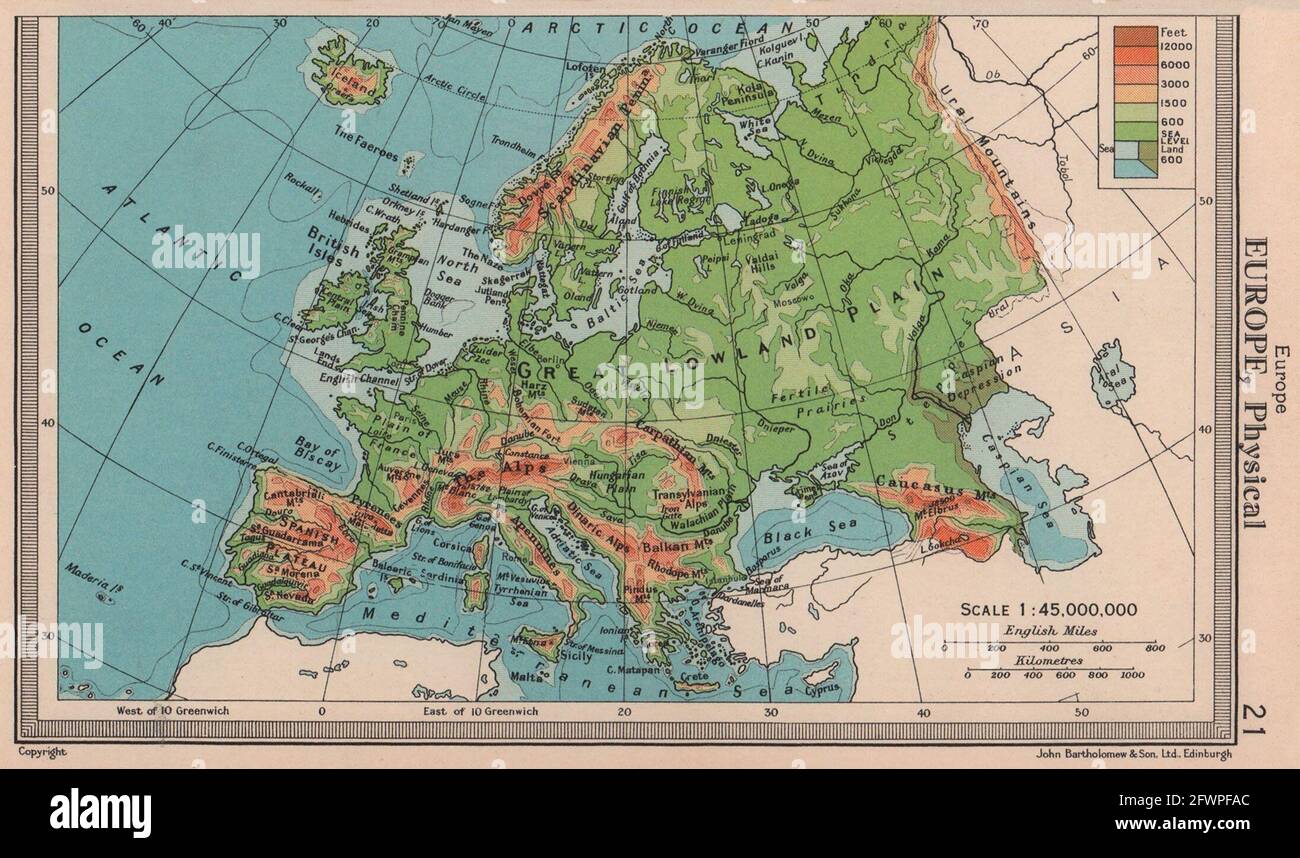
Europe’s mountains, towering giants etched across the continent, are not just dramatic landscapes but also crucial geological features. They influence weather patterns, create diverse ecosystems, and hold cultural and historical significance.
Major Mountain Ranges:
- The Alps: Stretching across eight countries, the Alps are the highest mountain range in Europe, home to iconic peaks like Mont Blanc and Matterhorn. They are a popular destination for skiing, hiking, and mountaineering.
- The Pyrenees: These mountains form a natural border between France and Spain, known for their rugged terrain and diverse ecosystems.
- The Carpathians: These mountains extend through Eastern Europe, traversing through countries like Romania, Slovakia, and Ukraine. They are home to dense forests and diverse wildlife.
- The Apennines: The Apennines run along the length of the Italian peninsula, forming a dramatic backdrop to the country’s diverse landscapes.
- The Scandinavian Mountains: Stretching across Norway and Sweden, these mountains are known for their jagged peaks, glaciers, and fjords.
Significance of Mountains:
- Climate and Weather: Mountains influence weather patterns by creating rain shadows and altering air circulation. They often act as barriers, blocking the passage of clouds and precipitation.
- Biodiversity: Mountains harbor diverse ecosystems, ranging from alpine meadows to dense forests. They are home to unique flora and fauna adapted to harsh conditions.
- Water Resources: Mountains are important sources of water, as they act as natural reservoirs, storing snow and ice that melt and feed rivers.
- Tourism and Recreation: Mountains attract tourists from around the world for activities like skiing, hiking, mountaineering, and nature exploration.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Mountains have long held cultural and historical significance, often serving as natural borders and providing inspiration for myths and legends.
The Interplay of Rivers and Mountains: A Symphony of Nature
The rivers and mountains of Europe are not isolated entities; they are intertwined in a dynamic and complex relationship. Mountains act as sources of water, feeding rivers that flow through valleys and plains. Rivers, in turn, shape the landscapes they traverse, carving valleys, creating fertile plains, and influencing local climates.
Examples of Interplay:
- The Alps and the Rhine: The Rhine River originates in the Swiss Alps, where snowmelt feeds its flow. The river then carves its way through the Alps, creating dramatic gorges and fertile valleys.
- The Pyrenees and the Ebro: The Ebro River originates in the Pyrenees Mountains, where snowmelt and rainfall feed its flow. The river then flows through Spain, creating fertile farmland and providing water for irrigation.
- The Carpathians and the Danube: The Danube River receives water from numerous tributaries that flow from the Carpathian Mountains, contributing to its volume and importance as a waterway.
This intricate interplay between rivers and mountains has shaped Europe’s physical landscape, created diverse ecosystems, and influenced human settlements and development throughout history.
Understanding the Map: A Tool for Exploration
A map of Europe’s rivers and mountains is more than just a static representation of geographical features. It is a tool for understanding the complex interplay of these elements and their impact on the continent’s history, culture, and environment.
Benefits of Using a Rivers and Mountains Map:
- Visualizing Geographical Connections: A map helps visualize the interconnectedness of rivers and mountains, revealing how they influence each other and shape the landscape.
- Understanding Regional Differences: The map highlights regional variations in river systems and mountain ranges, providing insights into the unique characteristics of different parts of Europe.
- Planning Travel and Exploration: The map can be used to plan travel routes, identifying scenic areas, hiking trails, and waterways for exploration.
- Learning about History and Culture: By tracing the courses of rivers and the locations of mountains, one can gain a deeper understanding of historical events, cultural influences, and the development of human settlements.
- Appreciating the Natural World: A map serves as a reminder of the beauty and importance of Europe’s natural features, encouraging appreciation for the intricate relationships between rivers, mountains, and the human world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the longest river in Europe?
A: The longest river in Europe is the Volga, flowing through Russia and emptying into the Caspian Sea.
Q: Which mountain range is the highest in Europe?
A: The Alps are the highest mountain range in Europe, with Mont Blanc being the highest peak.
Q: How do rivers and mountains influence each other?
A: Mountains often act as sources of water for rivers, with snowmelt and rainfall feeding their flow. Rivers, in turn, shape the landscapes they traverse, carving valleys and creating fertile plains.
Q: What is the significance of the Danube River?
A: The Danube is a vital waterway for trade and transportation, connecting the Black Sea to the North Sea via canals. It also serves as a source of water for irrigation and hydroelectric power.
Q: What are some of the unique features of the Alps?
A: The Alps are known for their iconic peaks, glaciers, and diverse ecosystems. They are a popular destination for skiing, hiking, and mountaineering.
Tips for Using a Rivers and Mountains Map
- Use a detailed map: A map with clear labels for rivers and mountains is essential for understanding the landscape.
- Look for patterns: Observe how rivers flow and how mountains are arranged, identifying connections and relationships.
- Research specific features: Explore the history, culture, and significance of individual rivers and mountains.
- Combine with other resources: Use the map in conjunction with travel guides, websites, and books to enhance your understanding.
- Use the map to plan trips: Identify scenic areas, hiking trails, and waterways for exploration.
Conclusion
Europe’s rivers and mountains are not just geographical features; they are integral components of the continent’s identity. They have shaped its landscape, influenced its climate, and played a crucial role in the development of its history, culture, and economy. Understanding the interplay of these natural forces through the lens of a comprehensive map provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of Europe’s natural heritage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Europe: Understanding the Interplay of Rivers and Mountains. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply