Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped By Geography
Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped by Geography
Related Articles: Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped by Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped by Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped by Geography

Afghanistan, a landlocked country in Central Asia, is a nation defined by its rugged terrain, diverse landscapes, and strategic location. Understanding the geography of Afghanistan is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and ongoing challenges. This article delves into the intricate details of Afghanistan’s geography, exploring its physical features, climate, and the impact these factors have on the country’s development and stability.
A Land of Mountains and Deserts:
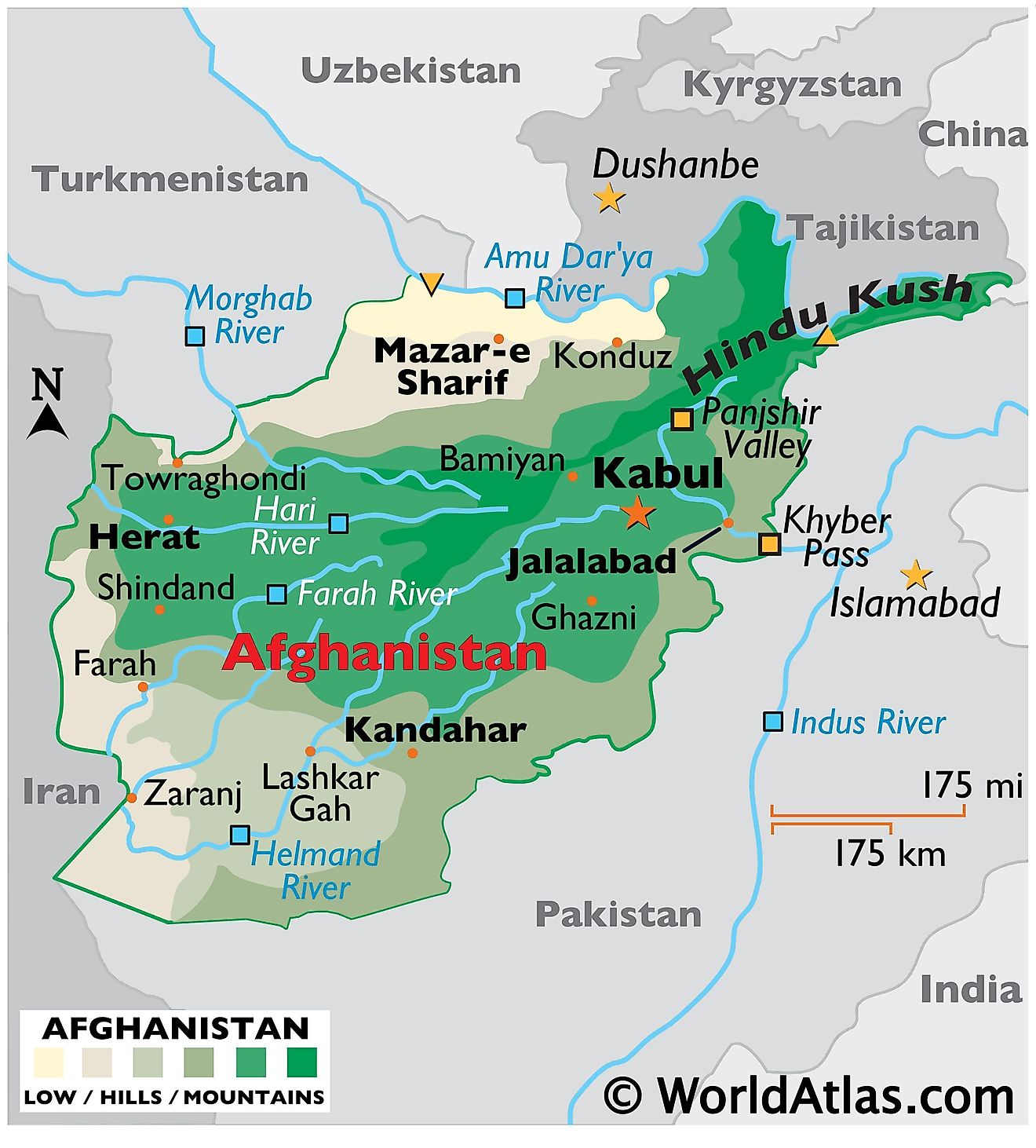
Afghanistan is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with the Hindu Kush mountain range dominating the country’s center. This range, reaching elevations exceeding 24,000 feet, acts as a natural barrier, dividing Afghanistan into distinct geographical regions. The towering peaks of the Hindu Kush are home to glaciers, which provide vital water resources for the surrounding valleys and rivers.
Beyond the Hindu Kush, Afghanistan’s landscape diversifies into vast plains, rolling hills, and arid deserts. The northern plains, known as the Amu Darya Valley, are fertile and support a significant portion of Afghanistan’s agricultural production. Conversely, the southwestern desert regions, including the Dasht-e Margo, are sparsely populated and characterized by harsh conditions.
A Tapestry of Diverse Climate Zones:
Afghanistan’s diverse geography translates into a wide range of climates. The mountainous regions experience cold winters with heavy snowfall, while the valleys and plains enjoy warmer temperatures. The southwestern deserts are characterized by extreme heat and aridity. This climatic diversity significantly influences agricultural practices, settlement patterns, and the country’s overall development.
Strategic Location and Regional Connectivity:
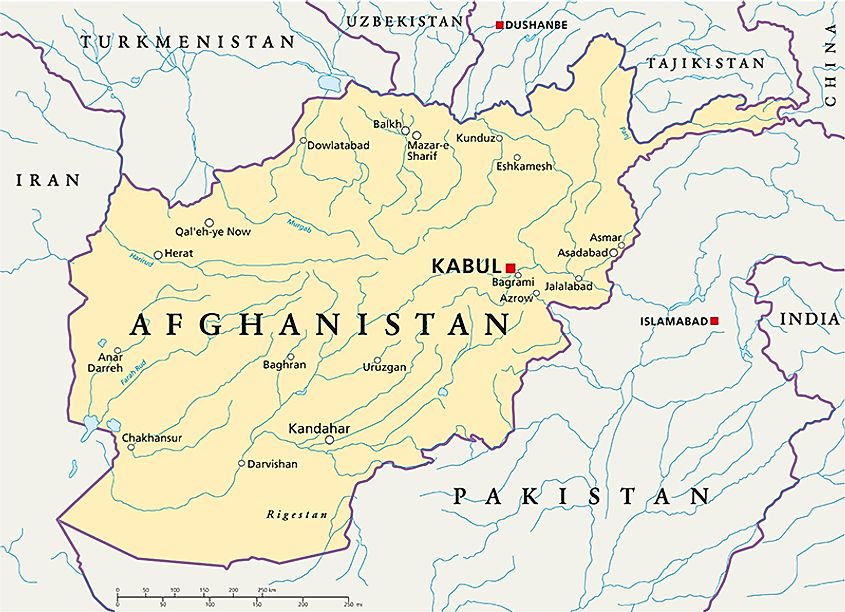
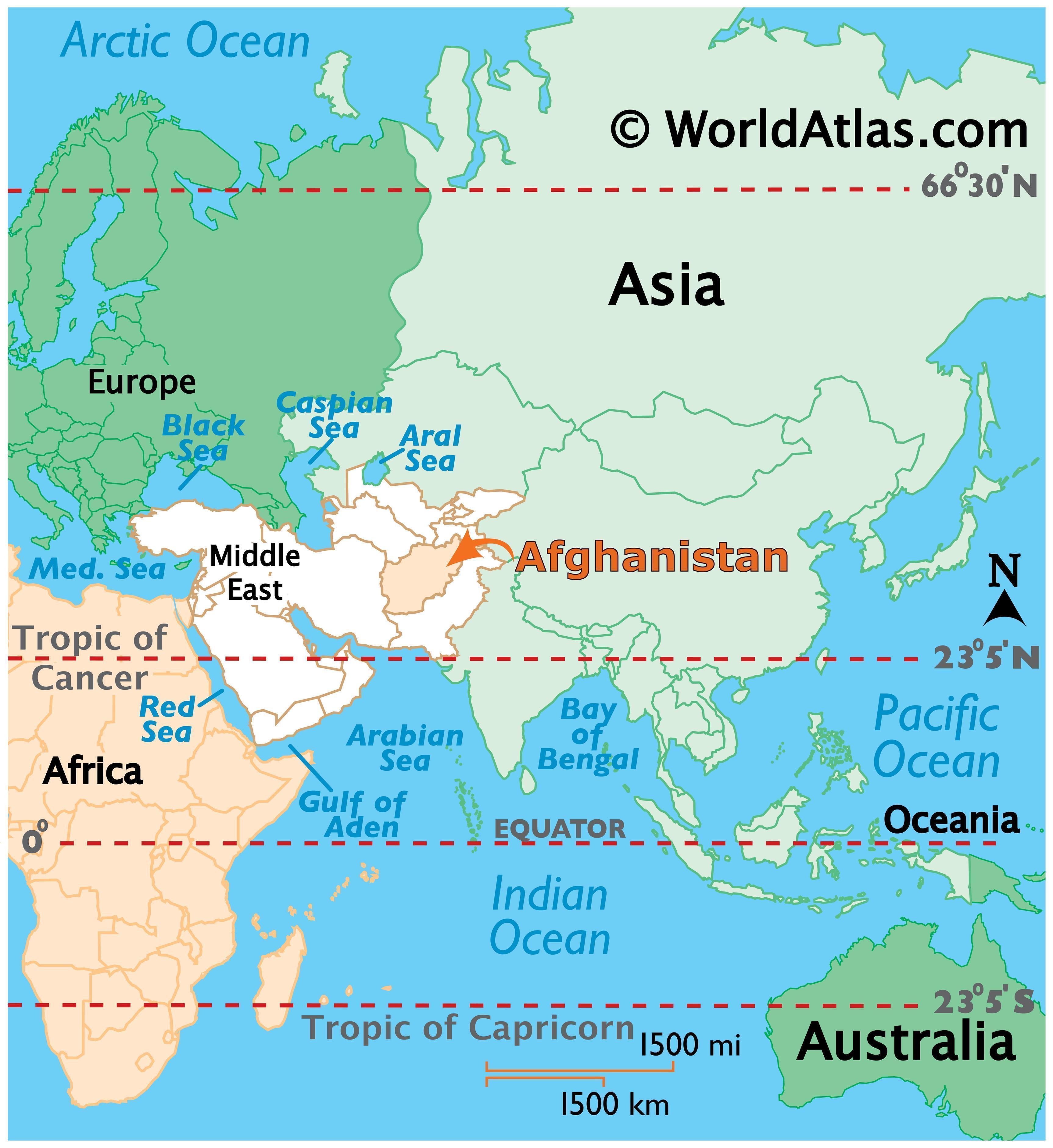
Afghanistan’s location at the crossroads of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East makes it strategically important. Its borders touch Iran, Pakistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China, connecting it to major trade routes and cultural spheres. This geographic position has historically played a pivotal role in shaping Afghanistan’s political and economic landscape.
Challenges of Terrain and Climate:
Despite its beauty and strategic significance, Afghanistan’s geography presents numerous challenges. The mountainous terrain hinders transportation and communication, isolating communities and hindering economic development. The arid climate and unpredictable rainfall patterns make agriculture vulnerable and susceptible to droughts.
Impact on Human Life and Development:
Afghanistan’s geography has a profound impact on human life and development. The mountainous regions are sparsely populated, with communities often reliant on subsistence agriculture and herding. The plains and valleys are more densely populated, supporting a wider range of economic activities. The country’s challenging terrain and climate have also contributed to ongoing conflicts and humanitarian crises.
The Importance of Understanding Afghanistan’s Geography:
Understanding the intricate details of Afghanistan’s geography is crucial for addressing the country’s multifaceted challenges. It provides insights into:
- Development Strategies: Tailoring development plans to the specific needs of different regions, considering their unique geographical characteristics.
- Resource Management: Utilizing water resources effectively, managing natural hazards, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
- Conflict Resolution: Recognizing the role of geography in shaping conflict dynamics and facilitating peacebuilding efforts.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Delivering aid efficiently and effectively, considering the challenges posed by terrain and climate.
- Cultural Understanding: Appreciating the diversity of Afghan society and the impact of geography on cultural practices and traditions.
FAQs about Afghanistan’s Geography:
Q: What is the highest mountain in Afghanistan?
A: The highest mountain in Afghanistan is Noshaq, with an elevation of 7,492 meters (24,580 feet).
Q: What are the main rivers in Afghanistan?
A: The main rivers in Afghanistan are the Amu Darya, the Helmand River, the Kabul River, and the Hari Rud River.
Q: What are the major geographical regions of Afghanistan?
A: The major geographical regions of Afghanistan include the Hindu Kush mountains, the Amu Darya Valley, the southwestern deserts, and the eastern highlands.
Q: How does Afghanistan’s geography affect its economy?
A: Afghanistan’s rugged terrain and lack of access to the sea pose significant challenges to economic development. Infrastructure development, transportation, and trade are all impacted by the country’s geographical features.
Q: What are the major natural resources found in Afghanistan?
A: Afghanistan has significant reserves of natural resources, including copper, iron ore, lithium, and natural gas. However, these resources remain largely untapped due to ongoing conflicts and infrastructure limitations.
Tips for Understanding Afghanistan’s Geography:
- Use online maps and satellite imagery: Explore interactive maps and satellite images to gain a better visual understanding of Afghanistan’s terrain and geographical features.
- Read books and articles: Consult academic resources and news articles that provide detailed information about Afghanistan’s geography, climate, and environmental issues.
- Watch documentaries: Explore documentaries and films that shed light on the lives of Afghans and the impact of their country’s geography on their livelihoods.
- Engage in discussions: Participate in online forums and discussions to learn from experts and share your own insights about Afghanistan’s geography.
Conclusion:
Afghanistan’s geography is a defining element of its identity, shaping its history, culture, and ongoing challenges. The country’s mountainous terrain, diverse landscapes, and strategic location have profoundly impacted its development, resource management, and political stability. By understanding the complexities of Afghanistan’s geography, we can gain valuable insights into the country’s past, present, and future, fostering a greater appreciation for its unique character and the challenges it faces.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Afghanistan: A Landlocked Nation Shaped by Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply