Charting The Rise Of An Empire: A Visual History Of Rome’s Expansion
Charting the Rise of an Empire: A Visual History of Rome’s Expansion
Related Articles: Charting the Rise of an Empire: A Visual History of Rome’s Expansion
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Rise of an Empire: A Visual History of Rome’s Expansion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Rise of an Empire: A Visual History of Rome’s Expansion

The Roman Empire, one of the most influential civilizations in human history, rose from humble beginnings to encompass a vast territory stretching from the British Isles to the Middle East. Understanding the geographical progression of Rome’s expansion is crucial for comprehending the empire’s political, social, and economic development. This article explores the visual narrative of Rome’s territorial growth, examining the key phases, motivations, and consequences of its remarkable expansion.
From City-State to Regional Power:
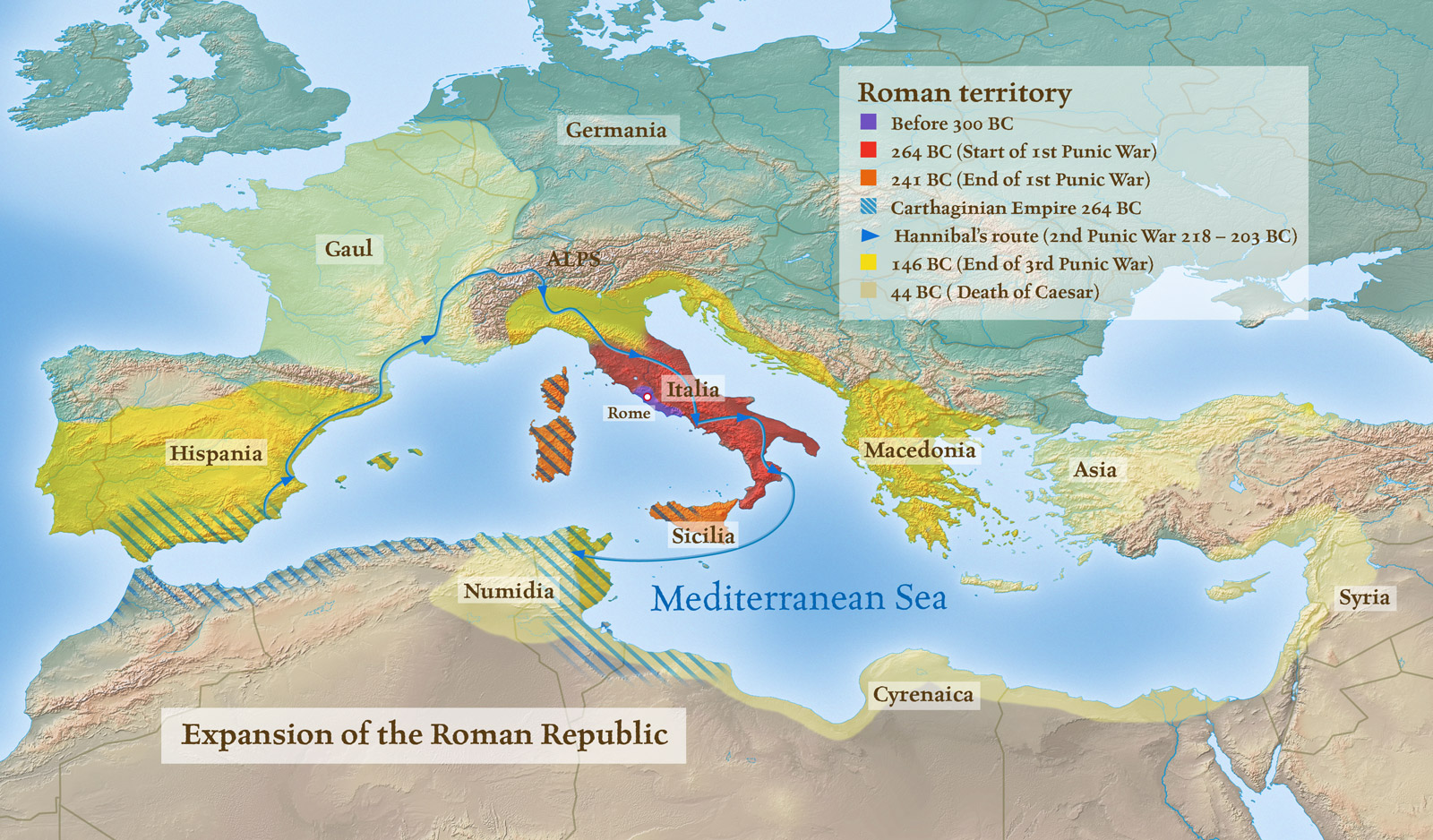
The early Roman Republic, established in 509 BCE, was initially a small city-state centered on the Tiber River. Its initial expansion was driven by a need for security and resources. The map below illustrates this early phase, with Rome’s influence gradually extending beyond the city walls, primarily in the Italian peninsula.
[Map of Rome’s initial expansion in the Italian peninsula, highlighting key conquests and territories acquired.]
The Punic Wars and Mediterranean Dominance:
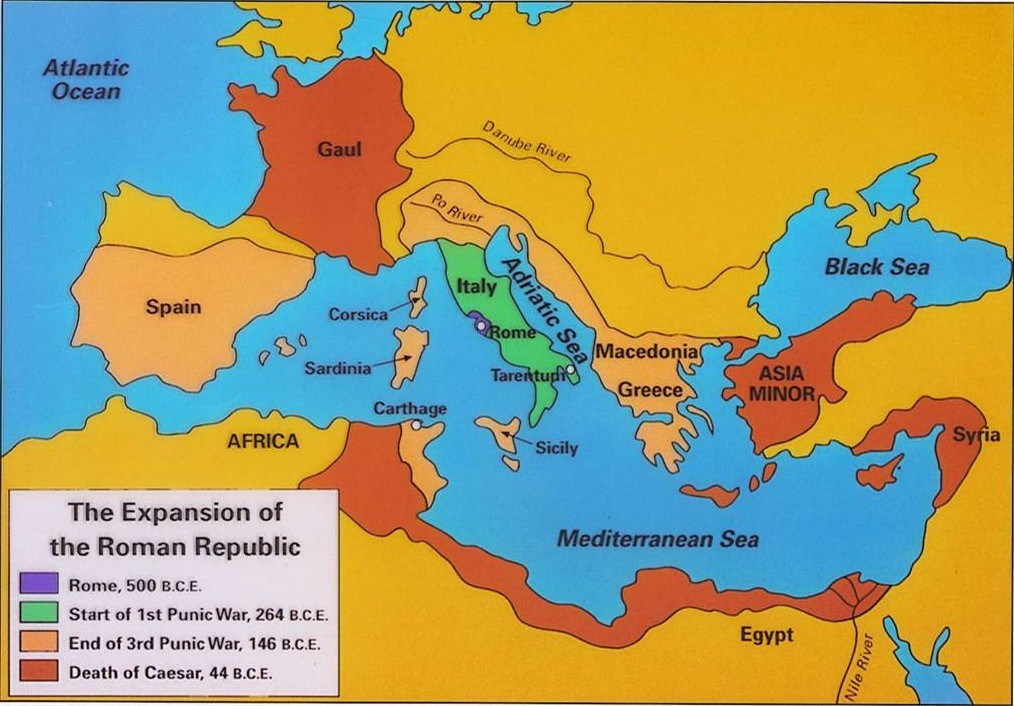
The clash between Rome and Carthage, known as the Punic Wars (264-146 BCE), marked a pivotal turning point in Rome’s expansion. The wars, fought over control of the western Mediterranean, resulted in Rome’s decisive victory and the acquisition of key territories in North Africa, Sicily, and Spain.
[Map depicting the Punic Wars, showcasing the territories controlled by Rome and Carthage, and the key battles fought.]
Expansion into the East:
The Roman Republic’s appetite for conquest extended beyond the Mediterranean basin. The conquest of Macedonia (168 BCE) and the subsequent defeat of the Seleucid Empire in the East (64 BCE) brought vast territories under Roman control. The incorporation of Greece and the Levant significantly enriched Roman culture and economy, integrating them into a vast network of trade and governance.
[Map highlighting the Roman conquests in the eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, the Levant, and Egypt.]
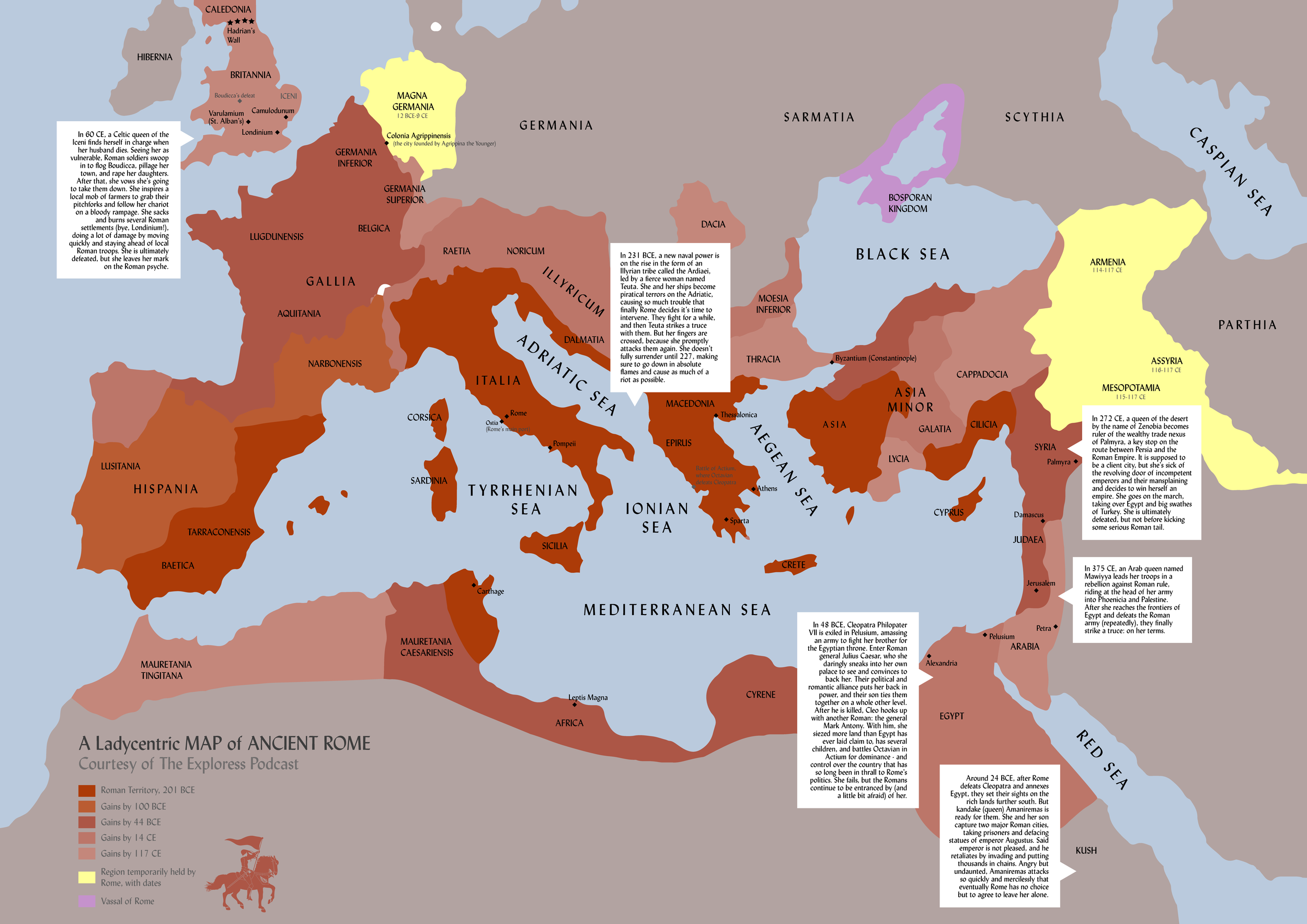
The Roman Empire and its Territorial Apex:
The transition from Republic to Empire under Augustus (27 BCE – 14 CE) marked a period of consolidation and further expansion. The empire reached its territorial peak under Emperor Trajan (98-117 CE), encompassing vast swathes of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
[Map showcasing the Roman Empire at its peak under Emperor Trajan, highlighting the boundaries of the empire and major provinces.]
Factors Driving Roman Expansion:
Several factors propelled Rome’s relentless expansion:
- Security: The Roman Republic, facing constant threats from neighboring tribes and rival city-states, sought to secure its borders and protect its citizens. Conquest was seen as a necessary means of achieving this goal.
- Resources: The pursuit of wealth and resources was a key driver of expansion. Rome sought to acquire fertile land, valuable minerals, and access to lucrative trade routes.
- Political Ambitions: Roman leaders, driven by ambition and the desire for glory, sought to expand the empire’s influence and power. Military victories and territorial gains were seen as a means of securing their political positions and legacy.
- Cultural Diffusion: Roman expansion facilitated the spread of Roman culture, language, and legal systems throughout the conquered territories. This cultural exchange fostered a sense of unity and common identity among the diverse populations of the empire.
Consequences of Roman Expansion:
The expansion of the Roman Empire had both positive and negative consequences:
- Prosperity and Stability: Roman rule brought peace and stability to many regions, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange. Infrastructure improvements, such as roads, aqueducts, and public buildings, facilitated trade and improved living standards.
- Cultural Integration: The Roman Empire facilitated the spread of Roman culture and legal principles, contributing to the development of a shared identity among its diverse populations.
- Exploitation and Oppression: The expansion of the Roman Empire often involved the exploitation and oppression of conquered peoples. Roman rule could be brutal, with heavy taxes and forced labor imposed on subject populations.
- Social and Political Instability: The vast size and complexity of the empire, along with the challenges of managing diverse populations and territories, contributed to social and political instability. Internal conflicts and rebellions became increasingly common, ultimately contributing to the empire’s decline.
FAQs about Rome’s Expansion:
1. What were the key factors that contributed to Rome’s initial expansion?
Rome’s early expansion was driven by a need for security, resources, and political ambition. The desire to protect its borders from neighboring tribes and rival city-states, coupled with the pursuit of fertile land, valuable minerals, and access to trade routes, fueled its territorial growth.
2. How did the Punic Wars impact Rome’s expansion?
The Punic Wars were pivotal in Rome’s expansion, marking its transition from a regional power to a Mediterranean empire. The decisive victory over Carthage granted Rome control of key territories in North Africa, Sicily, and Spain, significantly expanding its influence and resources.
3. What were the main challenges faced by Rome in managing its vast empire?
Managing a vast empire with diverse populations and territories posed significant challenges for Rome. Maintaining order and stability, ensuring the flow of resources, and navigating cultural differences were constant concerns for Roman rulers.
4. How did Roman expansion impact the cultural landscape of the Mediterranean world?
Roman expansion facilitated the spread of Roman culture, language, and legal systems throughout the conquered territories. This cultural exchange fostered a sense of unity and common identity among the diverse populations of the empire, shaping the cultural landscape of the Mediterranean world.
5. What were the long-term consequences of Rome’s expansion?
Roman expansion had both positive and negative consequences. It brought prosperity and stability to many regions, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange. However, it also involved exploitation and oppression of conquered peoples, contributing to social and political instability and ultimately contributing to the empire’s decline.
Tips for Understanding Rome’s Expansion:
- Study the maps: Visualizing Rome’s territorial growth through maps is crucial for understanding the geographical progression of its expansion and its impact on the world.
- Focus on key events: Identifying and understanding key events, such as the Punic Wars and the conquest of Gaul, helps to grasp the motivations and consequences of Rome’s expansion.
- Explore the cultural impact: Examining the cultural exchange facilitated by Roman expansion, including the spread of Roman language, law, and architecture, provides a deeper understanding of its legacy.
- Consider the social and political consequences: Analyzing the social and political challenges posed by managing a vast empire, including the potential for exploitation, oppression, and instability, offers a more nuanced perspective on Rome’s expansion.
Conclusion:
The map of Rome’s expansion is a visual testament to the empire’s remarkable rise to power. From a small city-state to a vast empire spanning continents, Rome’s territorial growth was driven by a complex interplay of factors, including security, resources, political ambition, and cultural exchange. While Roman expansion brought prosperity and stability to many regions, it also had its share of negative consequences, including exploitation, oppression, and ultimately, the empire’s decline. Understanding the geographical progression of Rome’s expansion provides valuable insights into the dynamics of empire building, the complexities of managing diverse populations, and the lasting impact of a civilization that shaped the course of Western history.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Rise of an Empire: A Visual History of Rome’s Expansion. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply