Delving Deeper: Process Maps Vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Process Maps: A Detailed Snapshot of Individual Processes
- 3.2 Value Stream Maps: A Holistic View of the Entire Value Chain
- 3.3 The Interplay of Process Maps and Value Stream Maps
- 3.4 FAQs: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Process Map and Value Stream Map Creation
- 3.6 Conclusion: Optimizing Operations with Process Maps and Value Stream Maps
- 4 Closure
Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide
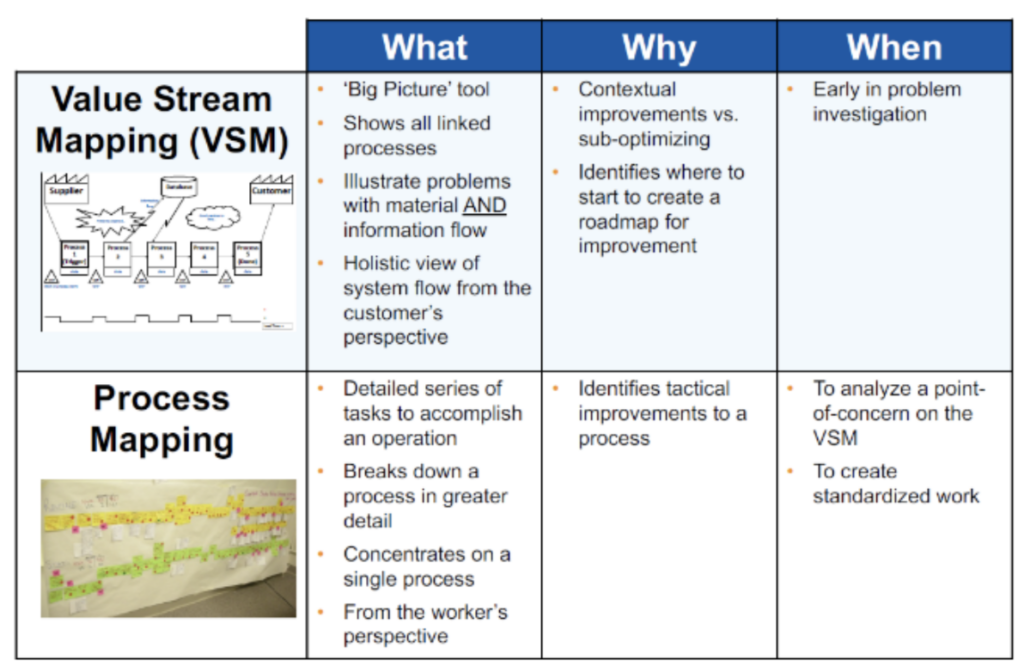
In the realm of process improvement and optimization, two powerful tools stand out: process maps and value stream maps. While both aim to visualize and analyze workflows, they differ in their scope, focus, and ultimate purpose. Understanding the distinction between these tools is crucial for businesses seeking to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and ultimately, deliver greater value to their customers.
Process Maps: A Detailed Snapshot of Individual Processes
Process maps, also known as flowchart diagrams, provide a detailed visual representation of a specific process. They depict the individual steps, activities, and decision points involved in completing a task or achieving a specific objective. This granular level of detail allows for a comprehensive understanding of how a process unfolds, highlighting potential areas for improvement and optimization.
Key characteristics of process maps:
- Focus: Individual processes, often within a single department or functional area.
- Scope: Narrow, focusing on the specific steps involved in a particular task.
- Level of Detail: High, showing individual activities and decision points.
- Purpose: Analyze and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of individual processes.
Benefits of using process maps:
- Improved process understanding: Process maps provide a clear and concise representation of how a process works, fostering a shared understanding among all stakeholders.
- Identification of inefficiencies: By visualizing the process flow, bottlenecks, redundancies, and unnecessary steps become readily apparent.
- Process standardization: Process maps serve as a blueprint for standardizing processes, ensuring consistency and predictability in execution.
- Enhanced communication: Process maps facilitate clear communication about process flow and responsibilities, reducing ambiguity and fostering collaboration.
- Documentation and training: Process maps serve as valuable documentation for training new employees and ensuring consistent process execution.
Examples of process maps:
- Order fulfillment process: Depicting the steps involved from receiving an order to shipping the product.
- Customer onboarding process: Illustrating the steps required to bring a new customer on board.
- Product development process: Mapping out the stages from idea generation to product launch.
Value Stream Maps: A Holistic View of the Entire Value Chain
Value stream maps, on the other hand, take a broader perspective, encompassing the entire value chain from the customer’s perspective. They visualize the flow of value from raw materials to the end customer, encompassing all activities, both value-adding and non-value-adding, involved in delivering a product or service.
Key characteristics of value stream maps:
- Focus: The entire value chain, encompassing all processes involved in delivering value to the customer.
- Scope: Broad, spanning multiple departments and functions.
- Level of Detail: Moderate, focusing on the flow of value and identifying waste.
- Purpose: Analyze and optimize the overall value stream, eliminating waste and improving customer value.
Benefits of using value stream maps:
- End-to-end process visibility: Value stream maps provide a holistic view of the entire value chain, highlighting inefficiencies and waste across different departments.
- Waste identification and elimination: By mapping the flow of value, non-value-adding activities become readily apparent, enabling their elimination and optimization.
- Lead time reduction: Value stream mapping helps identify and eliminate delays and bottlenecks, reducing lead time and improving overall efficiency.
- Customer value enhancement: By focusing on the flow of value, value stream maps facilitate the creation of products and services that truly meet customer needs.
- Improved collaboration: Value stream mapping fosters collaboration across departments, promoting a shared understanding of the value chain and its impact on customer satisfaction.
Examples of value stream maps:
- Product development value stream: Mapping the flow of value from raw materials to the delivery of a finished product.
- Customer service value stream: Visualizing the flow of value from customer inquiry to resolution.
- Software development value stream: Mapping the flow of value from requirements gathering to software deployment.
The Interplay of Process Maps and Value Stream Maps
Process maps and value stream maps are not mutually exclusive tools. They complement each other by providing different levels of detail and focusing on distinct aspects of process improvement.
- Process maps are used to analyze and improve individual processes, while value stream maps offer a holistic view of the entire value chain, identifying opportunities for systemic improvement.
- Process maps focus on efficiency and effectiveness within a specific process, while value stream maps prioritize customer value and waste elimination.
By using these tools in conjunction, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their processes, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately, deliver greater value to their customers.
FAQs: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps
Q1: What is the main difference between a process map and a value stream map?
A: Process maps focus on individual processes and their efficiency, while value stream maps encompass the entire value chain and prioritize customer value.
Q2: Which tool is better, process map or value stream map?
A: Both tools have their unique strengths and are valuable for different purposes. The choice depends on the specific objective and the scope of analysis.
Q3: Can I use both process maps and value stream maps together?
A: Yes, using both tools in conjunction can provide a comprehensive view of processes and identify opportunities for both process-level and system-wide improvement.
Q4: What are some examples of process maps and value stream maps?
A: Examples include order fulfillment process maps, customer onboarding process maps, product development process maps, product development value stream maps, customer service value stream maps, and software development value stream maps.
Q5: How can I create a process map or value stream map?
A: Various tools and techniques are available for creating process maps and value stream maps, including flowcharting software, sticky notes, and whiteboard sessions.
Tips for Effective Process Map and Value Stream Map Creation
- Clearly define the scope: Determine the specific process or value stream you wish to map.
- Involve relevant stakeholders: Engage individuals with firsthand knowledge of the process or value stream.
- Use clear and concise language: Employ simple and easily understandable terminology.
- Visually represent the flow: Utilize arrows, symbols, and colors to depict the flow of activities.
- Identify waste and inefficiencies: Analyze the map to identify areas for improvement and elimination of waste.
- Prioritize improvement opportunities: Focus on high-impact areas for optimization.
- Continuously monitor and update: Regularly review and update the maps to reflect changes in processes and workflows.
Conclusion: Optimizing Operations with Process Maps and Value Stream Maps
Process maps and value stream maps are powerful tools for process improvement and optimization. By providing different levels of detail and focusing on distinct aspects of value creation, these tools enable businesses to:
- Gain a deeper understanding of their processes.
- Identify and eliminate waste.
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Enhance customer value.
- Foster collaboration and communication.
By leveraging the insights gained from process maps and value stream maps, organizations can continuously strive for process excellence, ultimately delivering greater value to their customers and achieving sustainable growth.

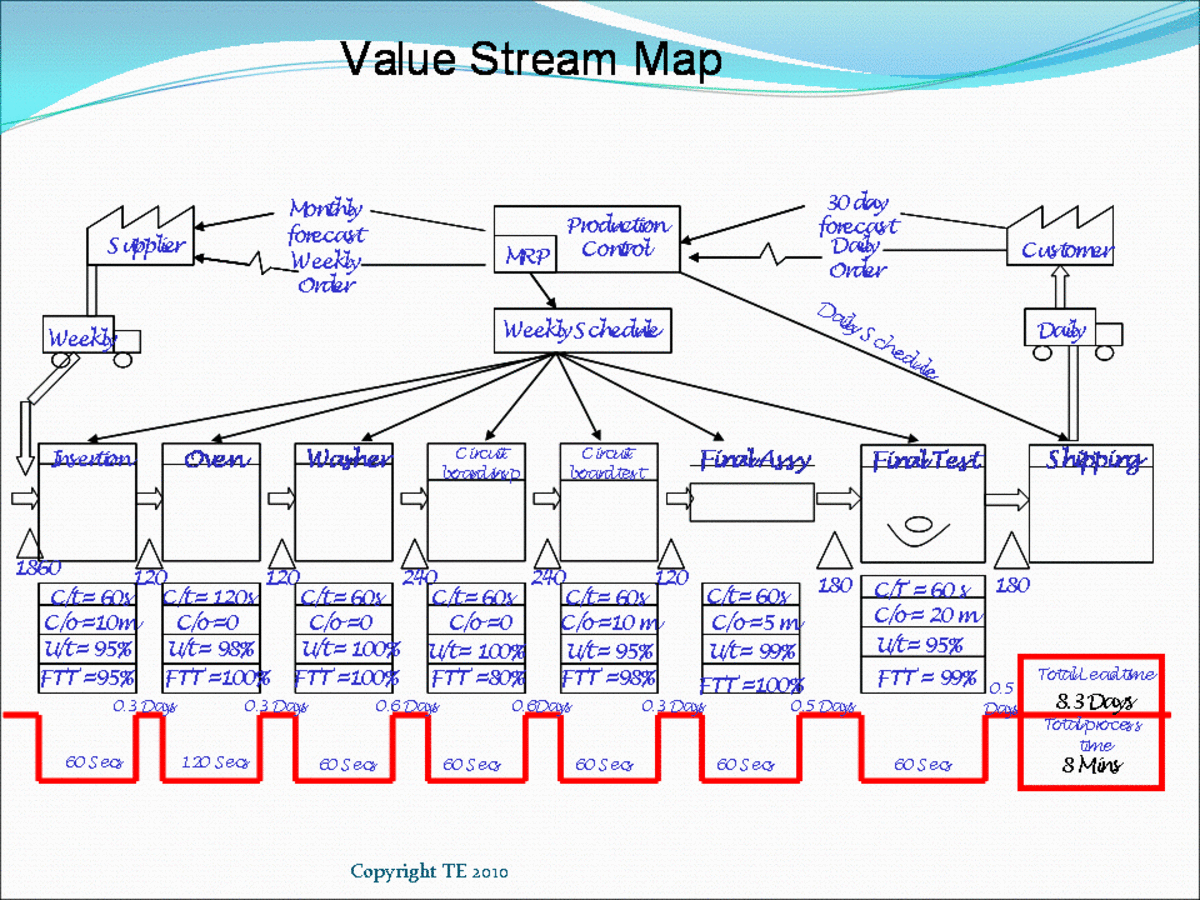
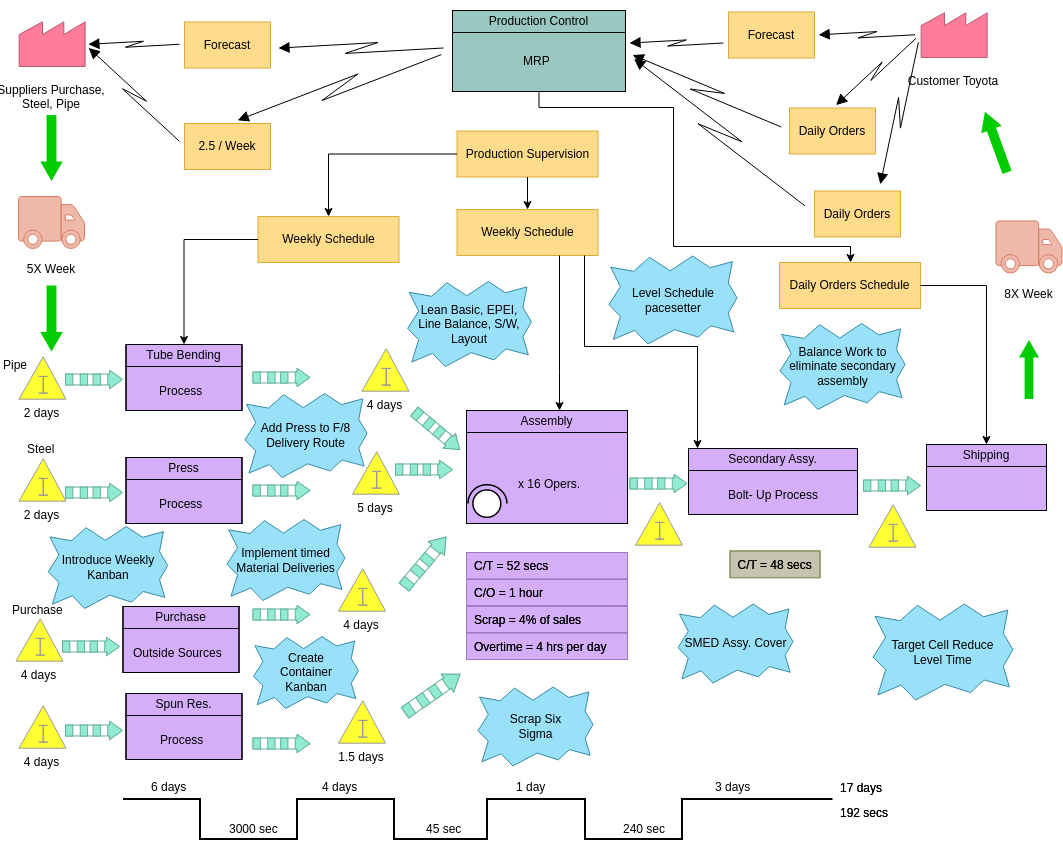
![[DIAGRAM] Process Flow Diagram Vs Value Stream Map - WIRINGSCHEMA.COM](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/g5wyGNPLMTc/maxresdefault.jpg)


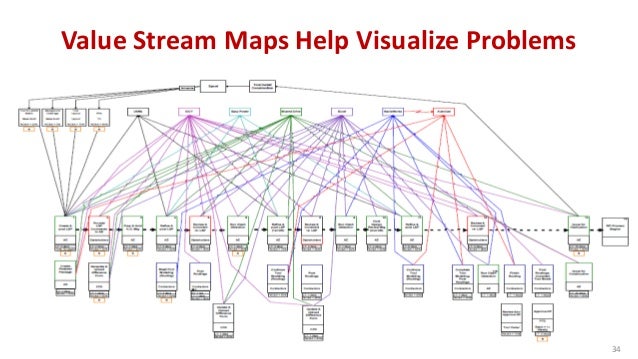

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving Deeper: Process Maps vs Value Stream Maps – A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply