Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive Into The Power Of The Map() Method
Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method
Related Articles: Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method
- 3.1 Understanding the map() Method: A Functional Approach
- 3.2 The Syntax of map(): A Simple Illustration
- 3.3 Practical Applications: Unlocking the Potential of map()
- 3.4 Examples: Illustrating the Power of map()
- 3.5 Beyond the Basics: Advanced map() Techniques
- 3.6 FAQs about JavaScript Array map()
- 3.7 Tips for Using map() Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map()
- 4 Closure
Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method

The map() method in JavaScript is a powerful tool for transforming arrays. It allows developers to create new arrays by applying a function to each element of an existing array, enabling efficient and elegant manipulation of data structures. This article will delve into the intricacies of the map() method, exploring its functionality, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the map() Method: A Functional Approach
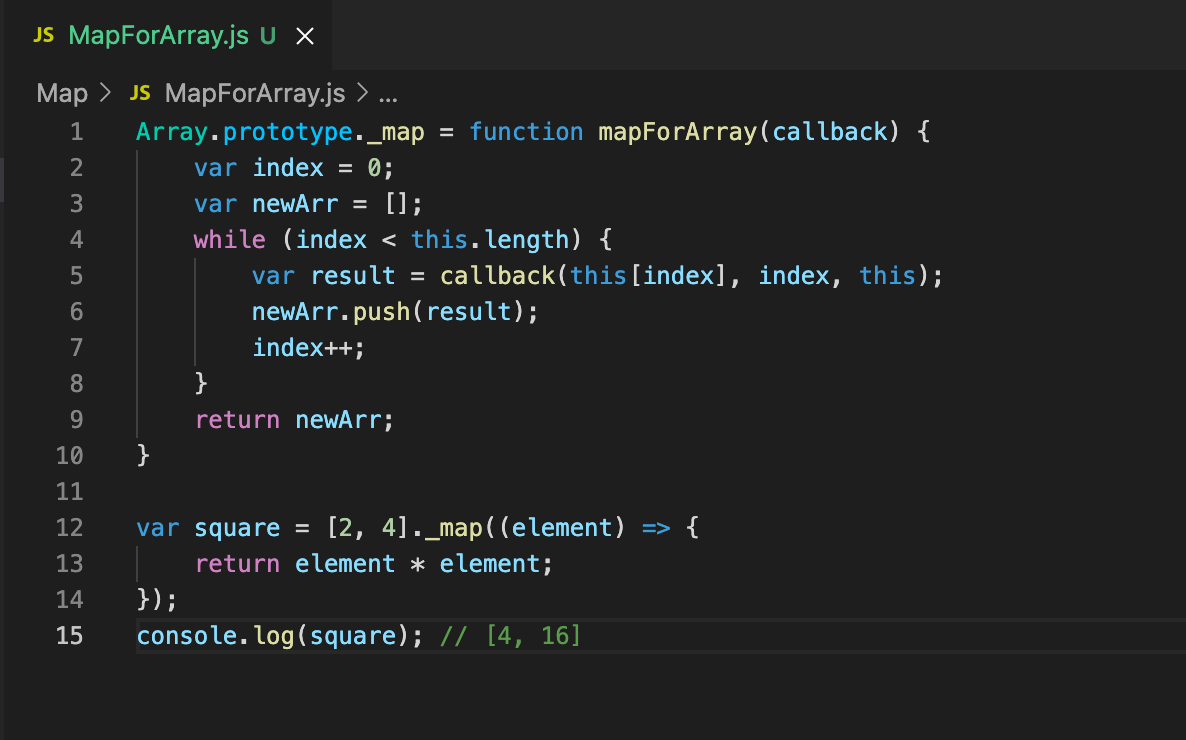
The map() method is a cornerstone of functional programming in JavaScript. Its core function is to iterate through each element of an array and apply a given function to it, returning a new array containing the results of these transformations. This approach offers several advantages:
-
Immutability: The
map()method operates on the principle of immutability, meaning it does not modify the original array. Instead, it creates a new array with the transformed elements, preserving the integrity of the original data. -
Readability: The functional nature of
map()promotes code clarity. The function being applied to each element is clearly defined, making it easier to understand the transformation logic. -
Efficiency: The
map()method is optimized for array manipulation, making it an efficient way to perform transformations on large datasets.
The Syntax of map(): A Simple Illustration
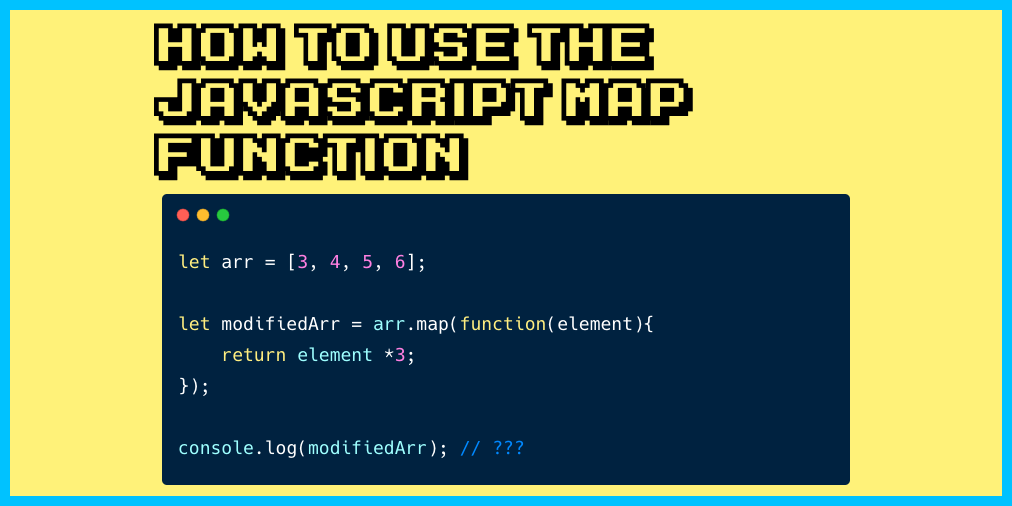
The syntax of the `map() method is straightforward:
const newArray = oldArray.map(function(element, index, array)
// Transformation logic
return transformedElement;
);-
oldArray: The original array on which the transformation will be applied. -
function(element, index, array): A function that takes three arguments:-
element: The current element being processed. -
index: The index of the current element in the array. -
array: The original array itself.
-
-
return transformedElement: The function must return the transformed value of the current element. -
newArray: The new array containing the transformed elements.
Practical Applications: Unlocking the Potential of map()
The map() method finds numerous applications across various JavaScript development scenarios. Here are some common use cases:
- Data Transformation: Converting data from one format to another, such as converting an array of strings to an array of numbers or vice versa.
-
Data Enrichment: Adding new properties to objects within an array. For example, adding a
priceproperty to each product object in an array of products. - Data Filtering: Creating a new array containing only the elements that meet specific criteria.
- String Manipulation: Applying transformations to strings within an array, such as capitalizing the first letter of each string.
- Array Manipulation: Performing complex operations on array elements, such as calculating the sum of all elements or finding the maximum value.
Examples: Illustrating the Power of map()
1. Data Transformation:
const temperaturesCelsius = [10, 20, 30, 40];
const temperaturesFahrenheit = temperaturesCelsius.map(celsius => (celsius * 9/5) + 32);
console.log(temperaturesFahrenheit); // Output: [50, 68, 86, 104]2. Data Enrichment:
const products = [
name: 'Apple', category: 'Fruit' ,
name: 'Banana', category: 'Fruit' ,
name: 'Milk', category: 'Dairy'
];
const enrichedProducts = products.map(product => (
...product,
price: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 1 // Random price between 1 and 10
));
console.log(enrichedProducts);3. Data Filtering:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const evenNumbers = numbers.map(number =>
if (number % 2 === 0)
return number;
);
console.log(evenNumbers); // Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]4. String Manipulation:
const names = ['john', 'jane', 'doe'];
const capitalizedNames = names.map(name => name.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + name.slice(1));
console.log(capitalizedNames); // Output: ['John', 'Jane', 'Doe']Beyond the Basics: Advanced map() Techniques
The map() method offers several advanced techniques that enhance its versatility:
-
Chaining: The
map()method can be chained with other array methods likefilter()andreduce(), enabling complex data transformations in a single, concise expression. -
Arrow Functions: Using arrow functions within the
map()method can significantly improve code readability and conciseness. -
Conditional Logic: Implementing conditional logic within the
map()function allows for selective transformations based on specific criteria. -
Nested Arrays: The
map()method can be used to transform elements within nested arrays, enabling complex data manipulations.
FAQs about JavaScript Array map()
1. Can I modify the original array using map()?
No, the map() method does not modify the original array. It creates a new array with the transformed elements, preserving the integrity of the original data.
2. What happens if the function within map() returns undefined?
If the function within map() returns undefined, the corresponding element in the new array will also be undefined.
3. Can I use map() with arrays of different data types?
Yes, the map() method can be used with arrays of different data types. The function within map() will handle the transformation logic based on the data type of each element.
4. How can I access the index of the element being processed within map()?
The map() method provides the index argument to the function being applied to each element. This argument represents the index of the current element in the array.
5. What are the advantages of using map() over a traditional for loop?
The map() method offers several advantages over a traditional for loop:
-
Readability: The
map()method is more concise and easier to read than aforloop. -
Immutability: The
map()method preserves the integrity of the original array, while aforloop can potentially modify it. -
Efficiency: The
map()method is optimized for array manipulation, making it more efficient than aforloop for large datasets.
Tips for Using map() Effectively
-
Avoid Side Effects: Ensure that the function within
map()does not have any side effects, such as modifying global variables or interacting with external APIs. - Clear Transformation Logic: Clearly define the transformation logic within the function being applied to each element.
-
Consider Chaining: Explore the possibility of chaining
map()with other array methods for more complex transformations. - Use Arrow Functions: Employ arrow functions for improved code readability and conciseness.
-
Test Thoroughly: Thoroughly test your
map()implementations to ensure they produce the desired results.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of map()
The map() method is a fundamental tool in JavaScript for transforming arrays. Its functional nature, immutability, and efficiency make it an invaluable asset for developers working with data structures. By understanding its functionality, exploring its practical applications, and mastering advanced techniques, developers can unlock the full potential of this powerful method and enhance the clarity, efficiency, and maintainability of their JavaScript code.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering JavaScript Array Transformations: A Deep Dive into the Power of the map() Method. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide

Leave a Reply