Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Highway Network
Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide to the Highway Network
Related Articles: Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide to the Highway Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide to the Highway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide to the Highway Network

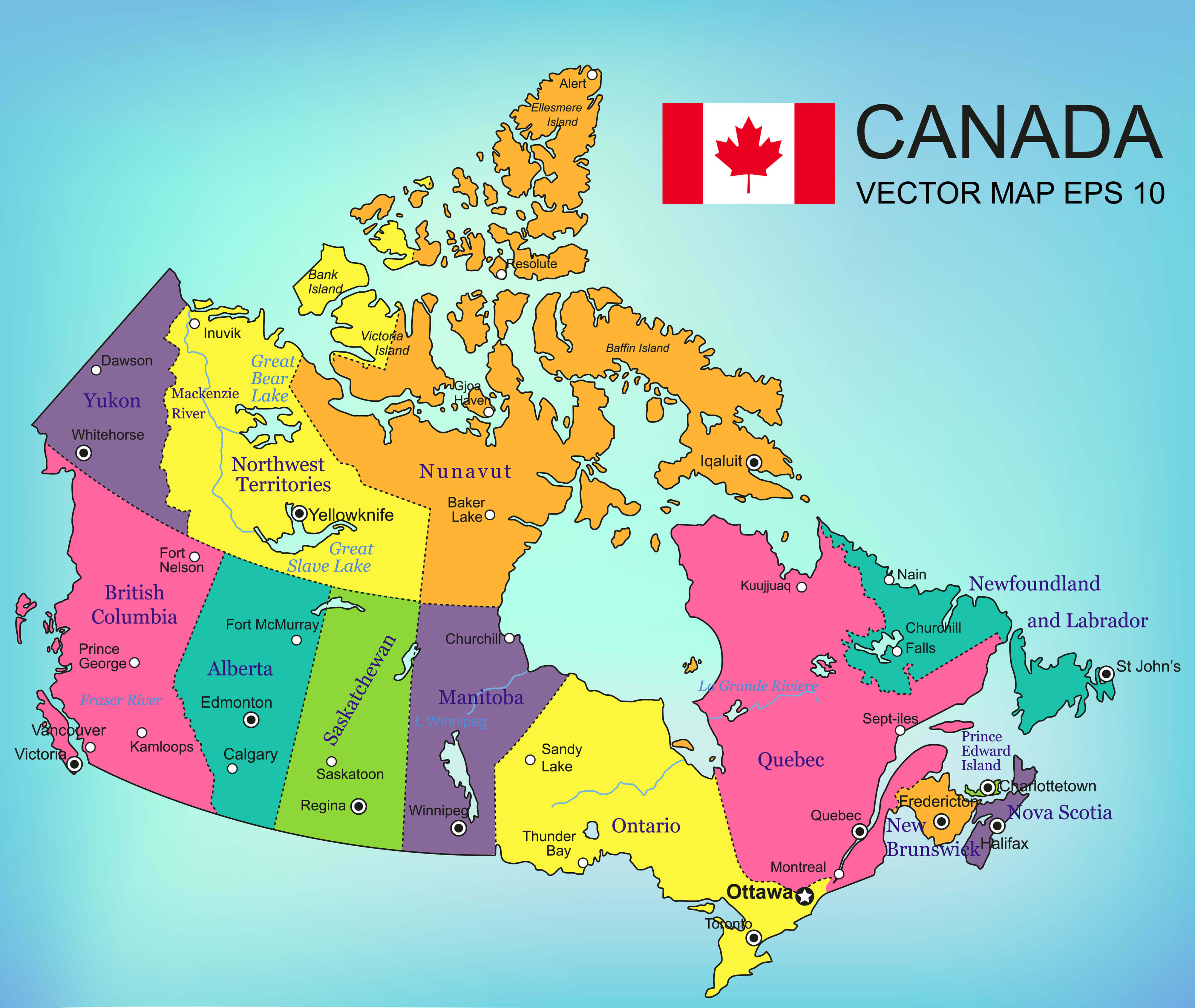
Canada, a vast and diverse country, boasts a complex and extensive network of highways that connect its provinces and territories. This network is crucial for facilitating trade, tourism, and the movement of people and goods across the country. Understanding the intricacies of this highway system is essential for anyone planning a road trip or simply seeking to navigate the vast landscapes of Canada.
A Glimpse into Canada’s Highway System
The Canadian highway system is a testament to the country’s vastness and the need to connect its far-flung regions. It comprises a diverse range of roads, from major transcontinental highways to smaller provincial and regional routes. The backbone of this system is the Trans-Canada Highway, a 7,821-kilometer route that stretches from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean, traversing all ten provinces.
Key Features of Canada’s Highway Network:
- Trans-Canada Highway (Highway 1): This iconic route is the longest national highway in the world, offering breathtaking views of Canada’s diverse landscapes. It serves as a vital artery for connecting major cities and providing access to national parks, scenic drives, and cultural attractions.
- Provincial and Territorial Highways: Each province and territory maintains its own network of highways, which are typically numbered according to a local system. These highways connect smaller towns and communities, providing access to local attractions and services.
- Interprovincial Highways: These highways connect different provinces and often form part of larger transcontinental routes. They are typically designated with a combination of letters and numbers, such as Highway 401 in Ontario, which is a major interprovincial route.
- Highway Maintenance: The responsibility for maintaining highways falls primarily on the provincial and territorial governments. This includes tasks such as snow removal, road repairs, and safety inspections.
Benefits of Canada’s Highway System:
- Economic Growth: The highway network facilitates the movement of goods and services, contributing to economic growth in various sectors. It enables efficient transportation of agricultural products, manufactured goods, and natural resources.
- Tourism Development: Highways provide access to popular tourist destinations, including national parks, scenic routes, and cultural attractions. This promotes tourism and generates revenue for local communities.
- Social Connectivity: The highway system connects people and communities across vast distances, fostering social and cultural exchange. It enables families to visit each other, businesses to connect with clients, and individuals to explore different parts of the country.
- Emergency Response: Highways play a crucial role in facilitating emergency response efforts during natural disasters or other crises. They provide access to affected areas and allow for the swift movement of emergency personnel and supplies.
Navigating Canada’s Highways:
- Maps and GPS: Utilizing reliable maps and GPS systems is essential for safe and efficient navigation. Many resources are available, including physical maps, online mapping services, and in-car navigation systems.
- Road Conditions: Checking road conditions before embarking on a journey is crucial, especially during winter months or inclement weather. Provincial and territorial transportation departments provide regular updates on road closures, weather advisories, and construction delays.
- Safety Precautions: Driving on Canadian highways requires adherence to safety regulations, including speed limits, traffic laws, and winter driving protocols. It is important to be aware of potential hazards such as wildlife crossings, road construction, and changing weather conditions.
- Fuel and Rest Stops: Planning fuel stops and rest breaks is essential for long journeys. Canada has a network of gas stations, rest areas, and roadside attractions located along major highways.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Canada’s Highway System:
Q: What are the main transcontinental highways in Canada?
A: The most prominent transcontinental highway is the Trans-Canada Highway (Highway 1), which stretches from St. John’s, Newfoundland and Labrador, to Victoria, British Columbia. Other major transcontinental routes include the Yellowhead Highway (Highway 16), the Trans-Labrador Highway (Highway 500), and the Trans-Taiga Road (Highway 11).
Q: What are the major highways in each province and territory?
A: Each province and territory has its own network of highways, with varying numbering systems. For example, Ontario has Highway 401, a major interprovincial route, while British Columbia has Highway 1, a scenic coastal route.
Q: What are the best scenic drives in Canada?
A: Canada offers numerous scenic drives, including the Cabot Trail in Nova Scotia, the Icefields Parkway in Alberta, and the Sea to Sky Highway in British Columbia. These routes provide breathtaking views of mountains, lakes, forests, and coastal landscapes.
Q: How can I find information about road closures and weather conditions?
A: Provincial and territorial transportation departments provide regular updates on road conditions through websites, social media, and mobile apps. You can also access information from radio stations, news websites, and travel websites.
Q: What are some tips for safe driving on Canadian highways?
A: Here are some tips for safe driving:
- Obey speed limits and traffic laws.
- Avoid distractions, such as mobile phones and texting.
- Take regular breaks to stay alert.
- Be aware of changing weather conditions and adjust your driving accordingly.
- Be prepared for wildlife crossings and road construction.
- Carry a winter survival kit, especially during winter months.
Conclusion:
Canada’s highway system is a vital infrastructure that plays a crucial role in connecting communities, facilitating economic growth, and promoting tourism. Understanding the nuances of this network, from major transcontinental routes to smaller provincial and regional highways, is essential for navigating the vast landscapes of Canada. By utilizing reliable maps, checking road conditions, and adhering to safety precautions, travelers can enjoy the benefits of this extensive highway network while ensuring a safe and enjoyable journey.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Canada: A Comprehensive Guide to the Highway Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply