Navigating Development In California: Understanding The Subdivision Map Act
Navigating Development in California: Understanding the Subdivision Map Act
Related Articles: Navigating Development in California: Understanding the Subdivision Map Act
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Development in California: Understanding the Subdivision Map Act. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Development in California: Understanding the Subdivision Map Act

The California Subdivision Map Act (SMA), enacted in 1969 and subsequently amended, serves as a crucial regulatory framework governing the division of land into smaller parcels for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes. Its purpose is to ensure that subdivisions are planned and developed in a manner that promotes public health, safety, and general welfare, while simultaneously protecting the environment and preserving natural resources.
This comprehensive legislation encompasses a wide range of aspects, including:
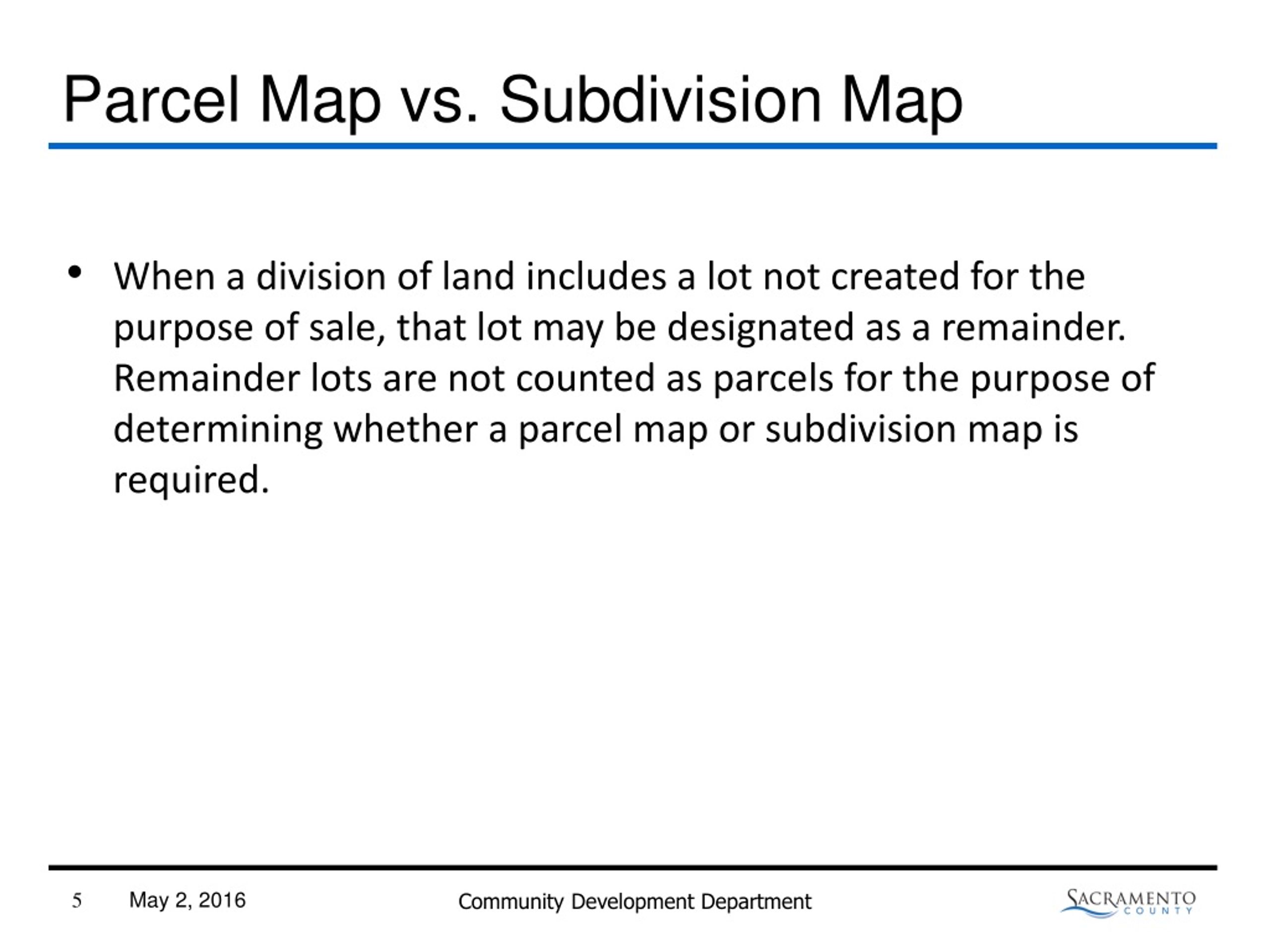
- Defining Subdivisions: The SMA meticulously defines what constitutes a subdivision, encompassing not only the traditional division of land into lots for sale but also the creation of condominium projects, planned unit developments (PUDs), and other forms of land division.
- Map Requirements: The Act mandates the preparation and approval of subdivision maps, which serve as blueprints for the development process. These maps detail the proposed layout of the subdivision, including lot sizes, street alignments, utilities, and other essential features.
- Environmental Review: The SMA emphasizes environmental considerations, requiring developers to conduct environmental impact assessments and obtain necessary permits to minimize adverse impacts on the surrounding environment.
- Public Input: Recognizing the importance of community engagement, the Act provides avenues for public hearings and review of proposed subdivisions, allowing residents to express their concerns and influence the development process.
- Enforcement: The SMA empowers local governments to enforce its provisions, ensuring compliance with regulations and addressing any violations that may occur.
The Importance of the Subdivision Map Act
The SMA plays a pivotal role in shaping the development landscape of California, contributing to the following benefits:
1. Promoting Orderly Development: By requiring developers to submit detailed maps and obtain necessary approvals, the Act ensures that subdivisions are planned and constructed in a coordinated manner, preventing haphazard development and ensuring consistency with local planning goals.
2. Protecting Public Health and Safety: The SMA mandates adherence to building codes, fire safety standards, and other regulations, guaranteeing that new developments meet minimum safety requirements and protect the health and well-being of residents.
3. Preserving Natural Resources: The Act’s emphasis on environmental review and mitigation measures helps to minimize the impact of development on sensitive ecosystems, protecting natural resources and promoting sustainable land use practices.
4. Enhancing Community Planning: By requiring public input and review of proposed subdivisions, the SMA fosters community engagement and allows residents to voice their concerns and influence the development process, contributing to a more inclusive and responsive planning process.
5. Ensuring Infrastructure Adequacy: The Act’s provisions concerning utilities, streets, and other infrastructure ensure that new subdivisions are equipped with the necessary infrastructure to support their residents and avoid overburdening existing infrastructure.
6. Preventing Fraud and Misrepresentation: The SMA’s requirements for detailed maps and disclosure of information help to prevent fraud and misrepresentation by developers, protecting potential buyers from misleading or incomplete information.
Understanding the Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The process of obtaining subdivision map approval under the SMA can be complex and involves several key steps:
- Preliminary Planning: Developers must begin by preparing a preliminary plan for the subdivision, outlining the proposed layout, lot sizes, and other key features.
- Environmental Review: An environmental impact assessment must be conducted to evaluate the potential environmental impacts of the proposed subdivision.
- Public Hearings: The developer must hold public hearings to provide an opportunity for residents to express their concerns and suggestions.
- Map Preparation: Based on the preliminary plan and public input, the developer prepares a detailed subdivision map, incorporating necessary modifications and revisions.
- Submission and Review: The map is submitted to the local government for review and approval.
- Approval or Denial: The local government reviews the map and may approve, deny, or conditionally approve the subdivision, based on compliance with the SMA and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Regarding the Subdivision Map Act
1. What types of land divisions are subject to the SMA?
The SMA applies to a wide range of land divisions, including:
- Subdivisions for sale: The division of land into lots for sale or lease.
- Condominiums: The creation of individual units within a larger building or complex.
- Planned unit developments (PUDs): Developments that combine residential, commercial, or industrial uses.
- Other land divisions: Any division of land that creates new parcels for sale or lease.
2. What are the requirements for obtaining subdivision map approval?
The specific requirements for obtaining subdivision map approval vary depending on the local jurisdiction and the type of subdivision. However, common requirements include:
- Preliminary plan: A detailed plan outlining the proposed subdivision layout.
- Environmental impact assessment: An assessment of the potential environmental impacts of the subdivision.
- Public hearings: Opportunities for public input and review of the proposed subdivision.
- Subdivision map: A detailed map of the subdivision, including lot sizes, street alignments, utilities, and other features.
- Compliance with local regulations: Adherence to local zoning ordinances, building codes, and other relevant regulations.
3. What are the consequences of violating the SMA?
Violations of the SMA can result in a variety of consequences, including:
- Fines: Monetary penalties for noncompliance with the Act’s provisions.
- Injunctions: Court orders prohibiting further development or construction.
- Criminal prosecution: In some cases, criminal charges may be filed for serious violations.
4. Who is responsible for enforcing the SMA?
The SMA is primarily enforced by local governments, such as cities and counties. However, the California Department of Housing and Community Development (HCD) also plays a role in overseeing the implementation of the Act.
5. What are the benefits of the SMA for developers?
While the SMA may seem restrictive, it offers several benefits for developers, including:
- Clear guidelines: The Act provides developers with clear guidelines and regulations, reducing uncertainty and facilitating the planning and development process.
- Enhanced marketability: Subdivision map approval demonstrates compliance with regulations and enhances the marketability of new developments.
- Reduced risk of legal challenges: Obtaining proper approvals helps to minimize the risk of legal challenges from residents or environmental groups.
Tips for Navigating the Subdivision Map Act
- Consult with a qualified professional: Engage an experienced land use attorney or planner to guide you through the complexities of the SMA and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
- Plan early and thoroughly: Begin the subdivision planning process early and conduct thorough research to understand the requirements and potential challenges.
- Engage with the community: Seek input from residents and address their concerns early in the process to foster a collaborative and supportive environment.
- Be prepared for environmental review: Conduct a comprehensive environmental impact assessment and be prepared to implement mitigation measures to minimize adverse impacts.
- Document everything: Maintain detailed records of all communications, meetings, and approvals to demonstrate compliance with the SMA.
Conclusion
The California Subdivision Map Act stands as a cornerstone of responsible land development in the state, ensuring that subdivisions are planned and built in a manner that promotes public health, safety, and environmental protection. While the Act can be complex, its provisions contribute to a more orderly and sustainable development process, balancing the needs of developers with the interests of the community and the environment. By understanding the requirements of the SMA and engaging with local officials and residents, developers can navigate the process effectively and contribute to the creation of well-planned and thriving communities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Development in California: Understanding the Subdivision Map Act. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply