Navigating The Border: A Comprehensive Look At The Virginia-West Virginia Map
Navigating the Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Virginia-West Virginia Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Virginia-West Virginia Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Virginia-West Virginia Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Virginia-West Virginia Map
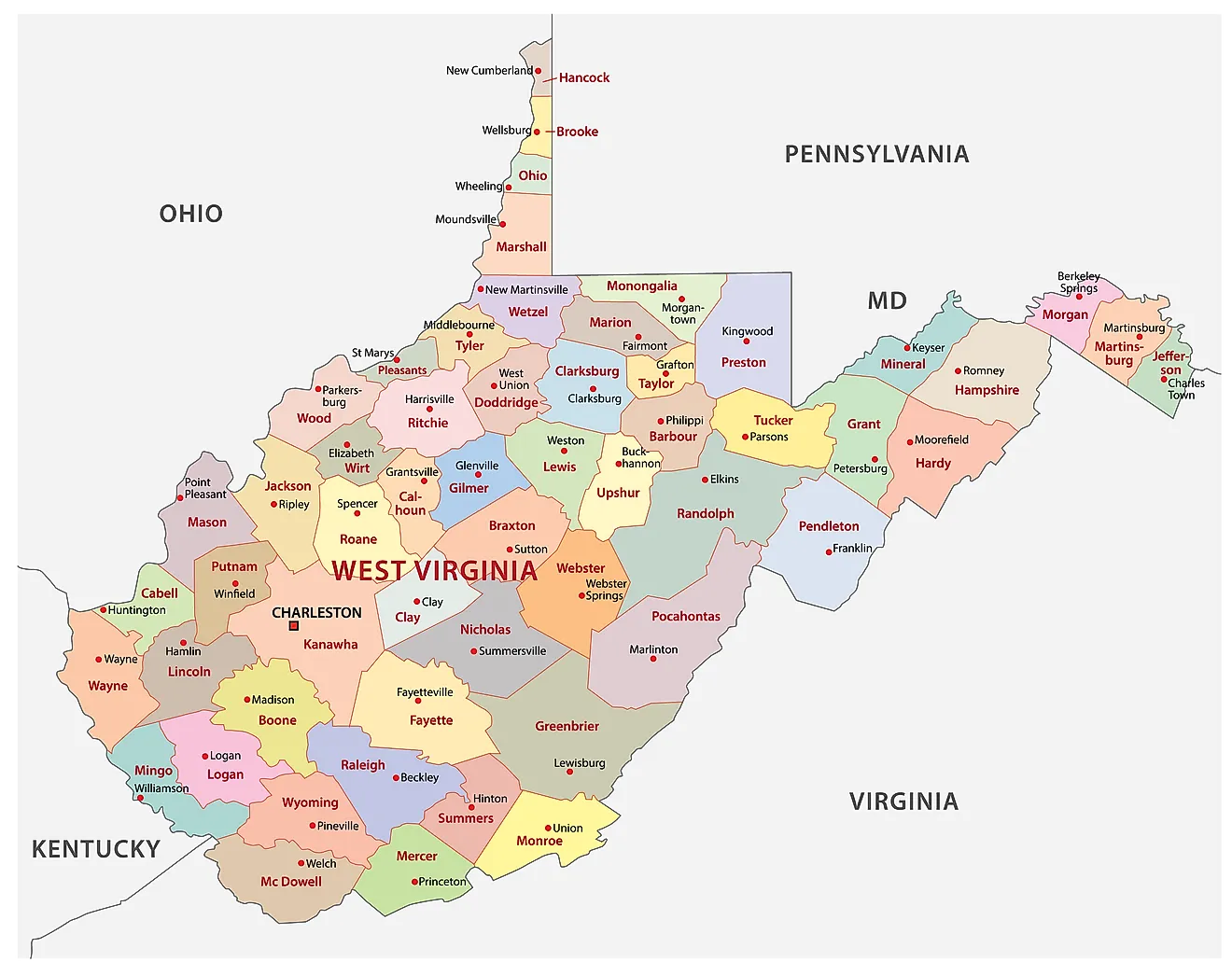
The shared border between Virginia and West Virginia is a fascinating tapestry of history, geography, and cultural exchange. Understanding the intricate relationship between these two states requires a thorough examination of their shared landscape, historical connections, and ongoing economic and social interactions. This article provides a detailed exploration of the Virginia-West Virginia map, highlighting its significance and impact on both states.
The Geography of the Border:
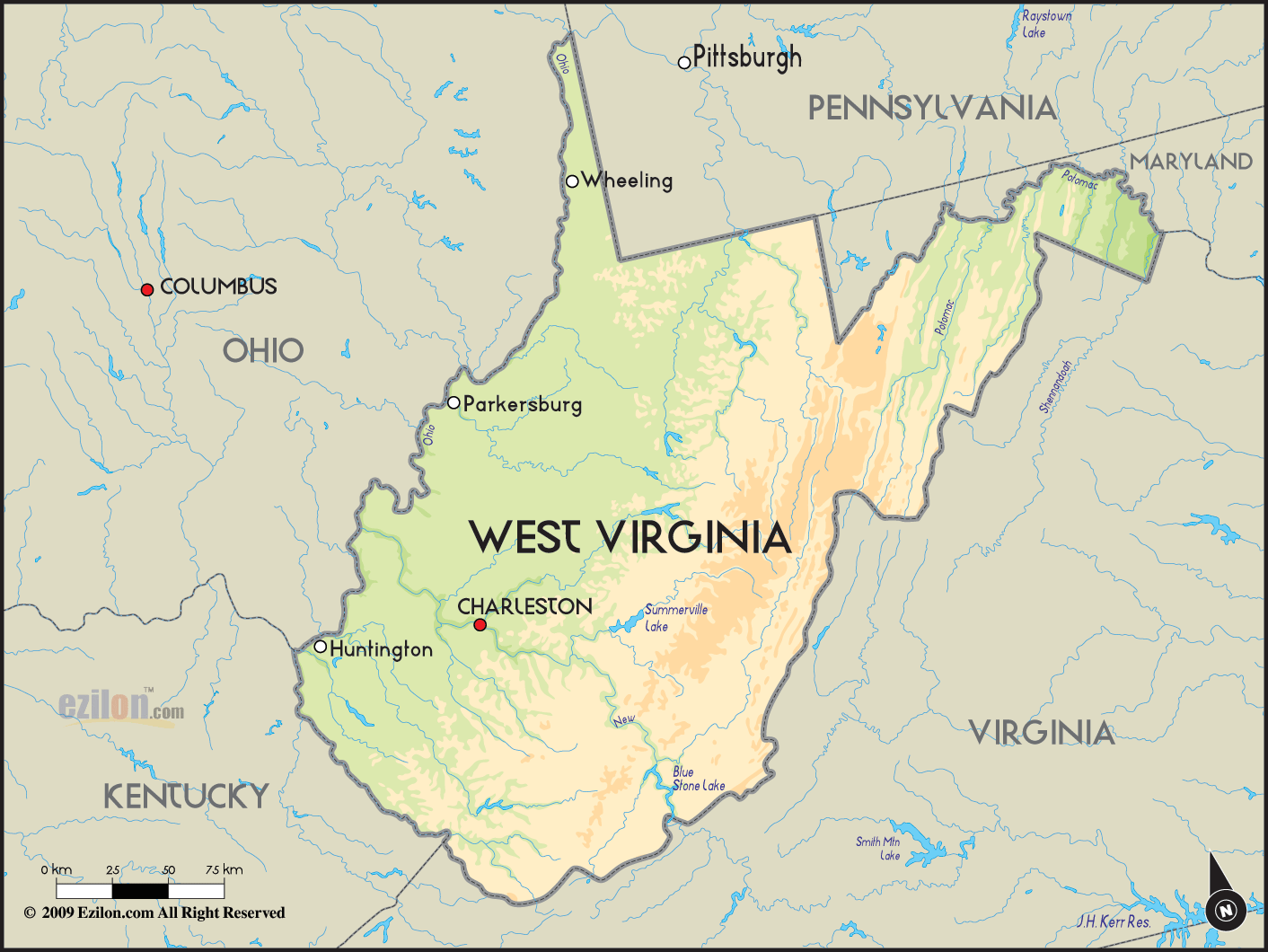
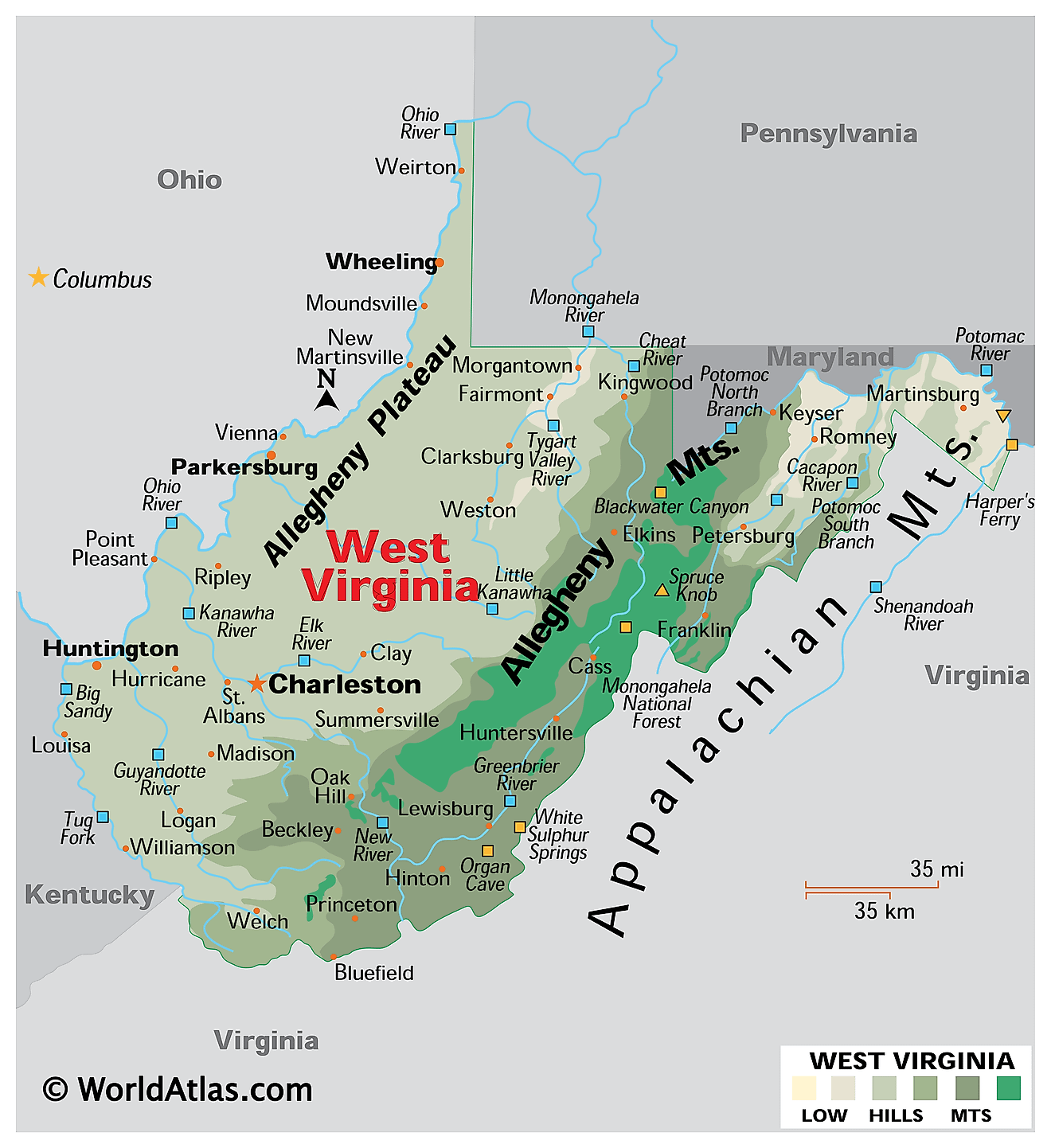
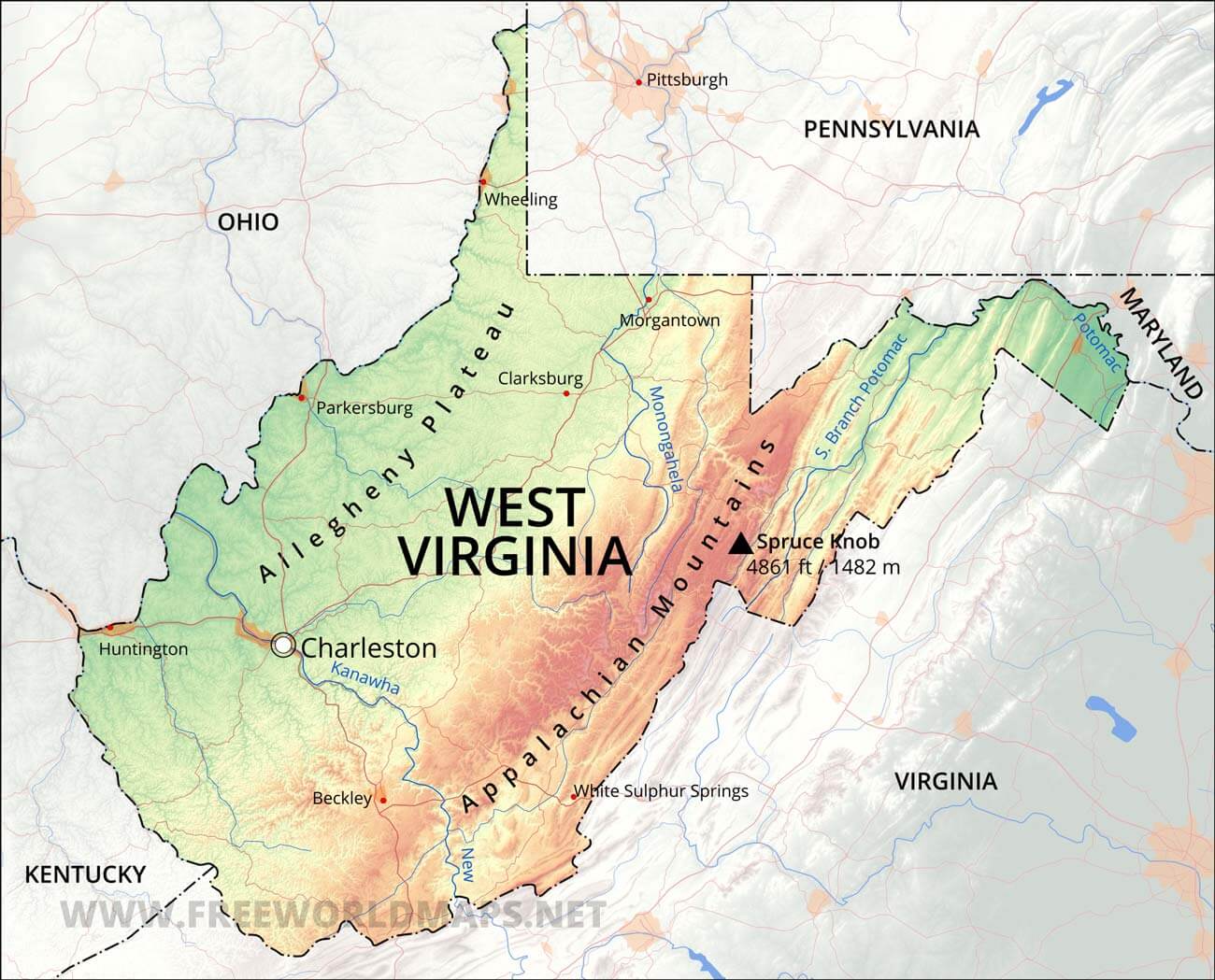
The border between Virginia and West Virginia is a winding line that stretches for approximately 420 miles, tracing the course of the Potomac River for a significant portion of its length. The Appalachian Mountains form a natural barrier, creating a rugged and diverse landscape. The border encompasses a variety of geographical features, including:
- The Potomac River: This major waterway serves as the primary boundary, flowing from its headwaters in the Appalachian Mountains eastward to the Chesapeake Bay. It is a vital resource for both states, providing drinking water, recreation opportunities, and transportation routes.
- The Appalachian Mountains: These ancient mountain ranges are a defining feature of the border, with peaks reaching elevations of over 4,000 feet. The mountains provide stunning scenery, diverse ecosystems, and valuable natural resources.
- The Shenandoah Valley: This fertile valley lies within the border, stretching westward from the Blue Ridge Mountains. It is known for its agricultural productivity, scenic beauty, and historical significance.
- The Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia: This region, situated to the east of the Appalachian Mountains, is geographically and culturally distinct from the rest of West Virginia. It shares a close relationship with neighboring counties in Virginia, particularly the Shenandoah Valley.
Historical Intertwining:
The Virginia-West Virginia border is a testament to the complex history of the region. Both states were originally part of the Colony of Virginia, which was established in 1607. In the 18th century, the western portion of Virginia became increasingly distinct, leading to a desire for separation and self-governance. In 1863, during the Civil War, West Virginia officially became a state, carving out a new identity from its Virginia roots.
Despite the separation, the historical ties between Virginia and West Virginia remain strong. The border is a reminder of shared heritage, including:
- Colonial history: Both states share a common colonial past, with the Virginia Company of London playing a significant role in their early development.
- Revolutionary War: The region witnessed numerous battles and campaigns during the American Revolution, with both Virginians and West Virginians fighting for independence.
- Civil War: The border became a focal point of the Civil War, with battles and skirmishes fought throughout the region.
Economic and Social Connections:
The Virginia-West Virginia border is not simply a geographical line; it is a dynamic zone of economic and social interaction. Both states rely on each other for resources, trade, and cultural exchange. Key connections include:
- Agriculture: The Shenandoah Valley, located within the border, is a major agricultural region, producing crops such as apples, corn, and livestock. Both Virginia and West Virginia benefit from this shared agricultural economy.
- Tourism: The scenic beauty of the Appalachian Mountains and the Shenandoah Valley attracts tourists from across the country. Both states have developed tourism industries that rely on the shared landscape.
- Energy: West Virginia is a major producer of coal, natural gas, and oil, while Virginia has significant hydroelectric power resources. Both states benefit from the exchange of energy resources.
- Transportation: The border is crisscrossed by major highways and railroads, facilitating the movement of goods and people between the two states.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Virginia-West Virginia border also presents challenges and opportunities for both states. Some key issues include:
- Economic disparities: West Virginia faces significant economic challenges, including high poverty rates and unemployment. This disparity creates challenges for both states in addressing regional development and social equity.
- Environmental concerns: The Appalachian Mountains are prone to environmental degradation, including mining pollution and deforestation. Both states must work together to protect the shared environment.
- Infrastructure needs: The border region requires investment in infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and broadband access, to promote economic development and improve quality of life.
- Cross-border cooperation: Effective cooperation between Virginia and West Virginia is essential to address shared challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Conclusion:
The Virginia-West Virginia map is more than just a line on a piece of paper; it is a symbol of shared history, geography, and cultural exchange. While the two states have distinct identities, they are inextricably linked by a shared landscape, historical heritage, and ongoing economic and social interactions. Understanding the complexities of the Virginia-West Virginia border is crucial for both states to navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
FAQs:
1. What are the major cities and towns located along the Virginia-West Virginia border?
The Virginia-West Virginia border encompasses a number of major cities and towns, including:
- Virginia: Winchester, Harrisonburg, Staunton, Martinsburg, and Front Royal.
- West Virginia: Martinsburg, Charles Town, Shepherdstown, Harpers Ferry, and Berkeley Springs.
2. What are the major industries located along the border?
The Virginia-West Virginia border is home to a diverse range of industries, including:
- Agriculture: Apples, corn, livestock, and dairy products.
- Tourism: Outdoor recreation, scenic drives, historical sites, and cultural events.
- Energy: Coal mining, natural gas production, and hydroelectric power.
- Manufacturing: Aerospace, automotive, and food processing.
3. What are the major transportation routes that cross the border?
The Virginia-West Virginia border is served by a network of major highways and railroads, including:
- Interstate 81: A major north-south highway connecting the Shenandoah Valley to the Northeast.
- Interstate 66: A major east-west highway connecting Washington, D.C., to the Shenandoah Valley.
- U.S. Route 11: A historic north-south highway running through the Shenandoah Valley.
- CSX Transportation: A major freight railroad that serves the region.
4. What are some of the historical sites located along the border?
The Virginia-West Virginia border is rich in history, with numerous historical sites, including:
- Harpers Ferry National Historical Park: A site of major significance during the Civil War and the abolitionist movement.
- Shenandoah National Park: A scenic park with hiking trails, waterfalls, and historical sites.
- George Washington’s Birthplace National Monument: The birthplace of the first President of the United States.
- Thomas Jefferson’s Poplar Forest: A plantation home designed by Thomas Jefferson.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing the border region?
The Virginia-West Virginia border faces a number of environmental challenges, including:
- Mining pollution: Coal mining operations can lead to water and air pollution.
- Deforestation: The removal of trees can lead to soil erosion, habitat loss, and reduced water quality.
- Climate change: The region is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as increased flooding and drought.
Tips for Exploring the Virginia-West Virginia Border:
- Plan your trip: Research the different attractions, activities, and lodging options available.
- Explore the outdoors: Hike the Appalachian Mountains, kayak the Potomac River, or visit a state park.
- Learn about history: Visit historical sites, museums, and battlefields.
- Sample the local cuisine: Enjoy fresh produce from the Shenandoah Valley, traditional Appalachian dishes, or craft beers.
- Support local businesses: Shop at local stores, restaurants, and craft breweries.
Conclusion:
The Virginia-West Virginia border is a dynamic and ever-evolving region. Understanding its history, geography, and economic and social connections is essential for appreciating its unique character. By recognizing the challenges and opportunities that exist along the border, both states can work together to build a more prosperous and sustainable future for the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Virginia-West Virginia Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply