Niger: A West African Nation At The Crossroads Of Cultures And Challenges
Niger: A West African Nation at the Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges
Related Articles: Niger: A West African Nation at the Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Niger: A West African Nation at the Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Niger: A West African Nation at the Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges
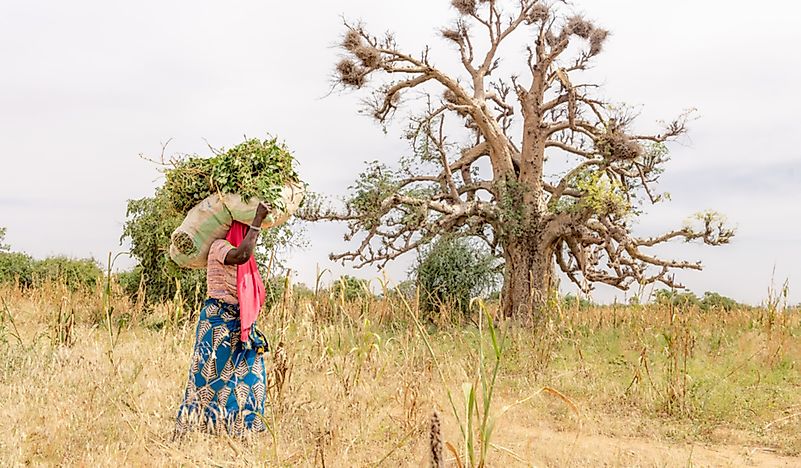

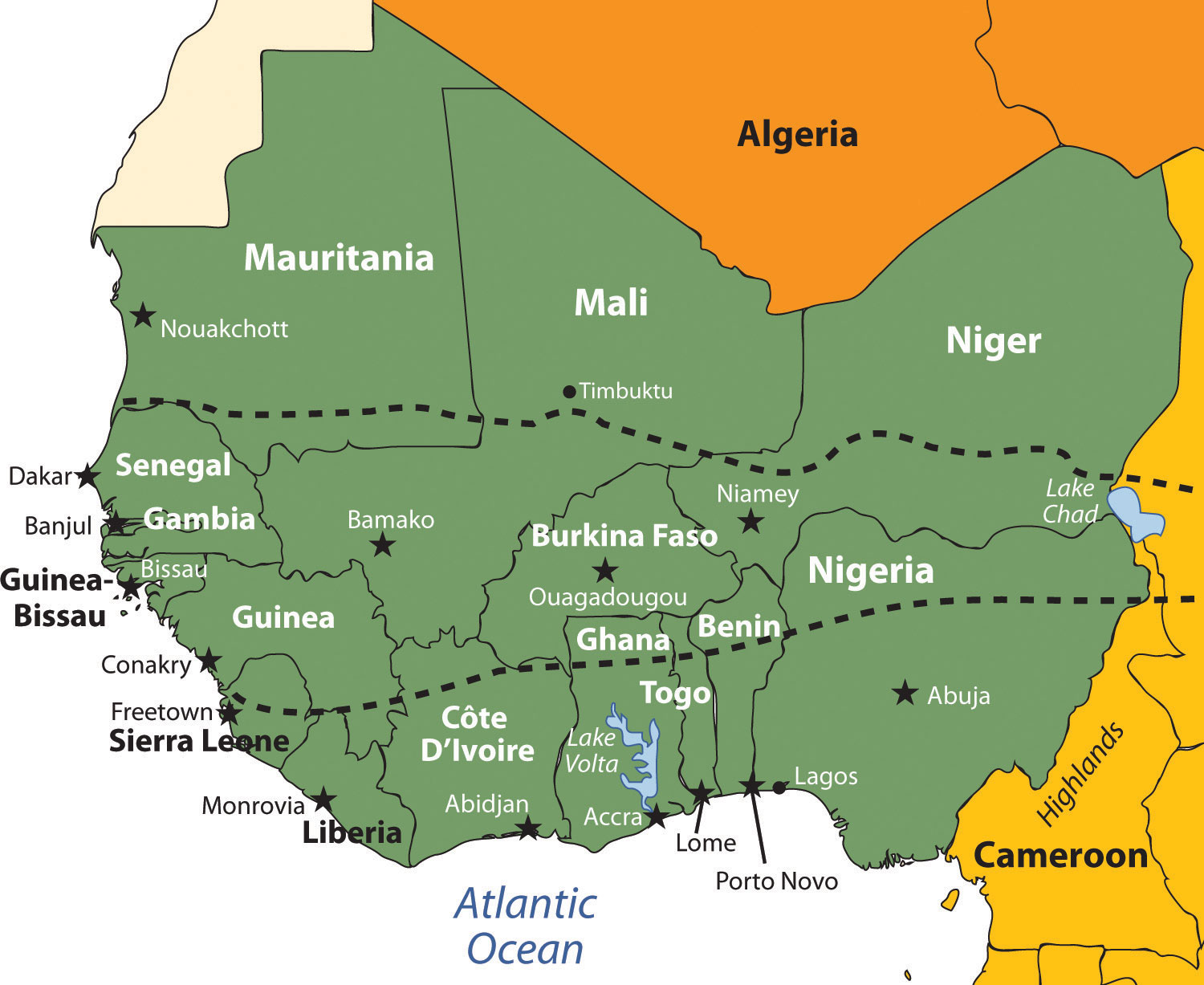
Niger, a landlocked nation in West Africa, occupies a significant position on the world map, not only geographically but also in terms of its cultural, economic, and geopolitical significance. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Niger, delving into its history, geography, culture, economy, and the challenges it faces, while highlighting its unique position in the broader African context.
A Land of Diverse Landscapes and Rich History
Niger’s landscape is a tapestry of contrasting elements, ranging from the vast Sahara Desert in the north to the fertile Sahel region in the south. The country’s geography plays a vital role in shaping its history, culture, and economic activities.
Geography and Climate:
- Sahara Desert: The northern region is dominated by the Sahara, the world’s largest hot desert, characterized by harsh conditions, extreme temperatures, and limited rainfall.
- Sahel Region: The southern region, known as the Sahel, marks a transition zone between the desert and the more humid savanna grasslands, offering a more hospitable environment for agriculture and human settlement.
- Aïr Mountains: Rising dramatically in the north-central region, the Aïr Mountains provide a unique and diverse ecosystem, home to a variety of flora and fauna.
- Niger River: The Niger River, which gives the country its name, flows through the southwestern region, providing a vital source of water for agriculture and transportation.
History and Culture:
- Ancient Civilizations: Niger’s history stretches back millennia, with evidence of ancient civilizations and empires, including the Kanuri Empire, the Songhai Empire, and the Bornu Empire.
- French Colonization: In the late 19th century, Niger was colonized by France, becoming part of French West Africa.
- Independence: Niger gained independence from France in 1960.
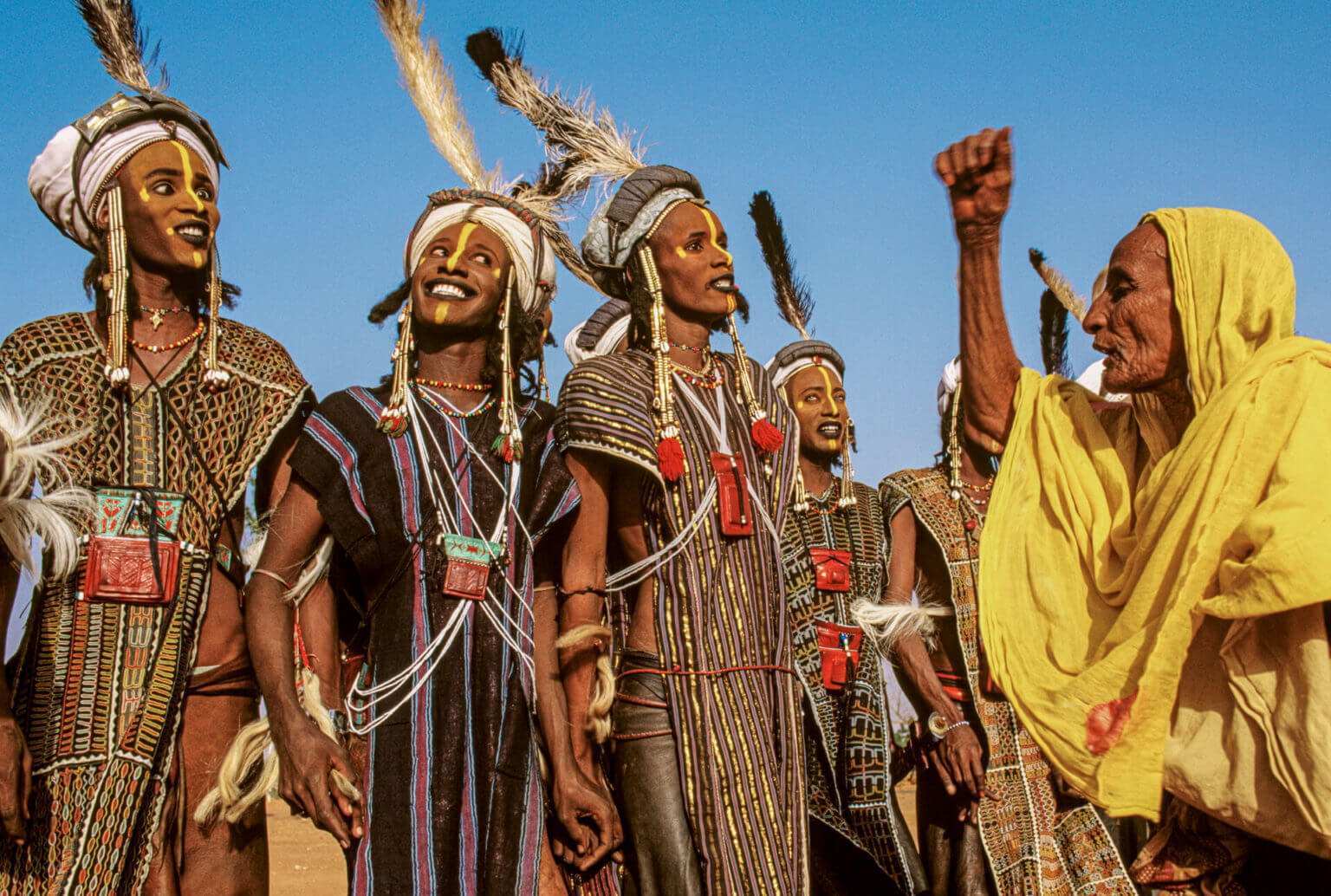
- Cultural Diversity: Niger is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and customs. The most prominent ethnic groups include the Hausa, the Zarma, the Tuareg, the Kanuri, and the Fulani.
Economy and Challenges
Niger’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture, livestock herding, and mining. Despite its vast natural resources, the country faces significant economic challenges, including poverty, food insecurity, and limited infrastructure.
Key Economic Sectors:
- Agriculture: Agriculture employs the majority of the workforce, with millet, sorghum, rice, and cowpeas being the main crops.
- Livestock Herding: Livestock herding is another crucial economic activity, with cattle, sheep, goats, and camels being raised for meat, milk, and hides.
- Mining: Niger possesses significant mineral resources, including uranium, gold, and coal. Uranium is a key export commodity, contributing significantly to the country’s revenue.
- Energy: Niger is a major producer of uranium, which is used in nuclear power plants. The country also has potential for renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
Challenges:
- Poverty: Niger has one of the highest poverty rates in the world, with a large portion of the population living below the poverty line.
- Food Insecurity: Droughts, desertification, and climate change pose significant threats to food security, leading to recurrent famines and malnutrition.
- Limited Infrastructure: Lack of adequate infrastructure, including roads, electricity, and water systems, hinders economic development and limits access to basic services.
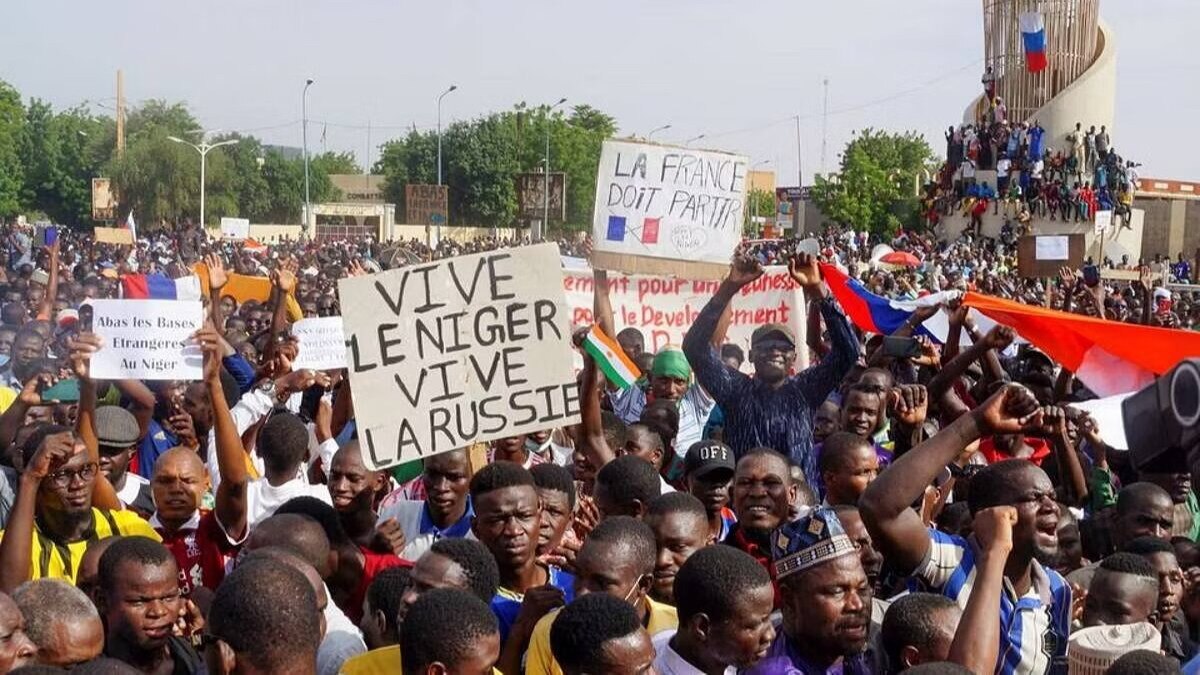
- Political Instability: Niger has experienced political instability and conflict, including armed rebellions and coups d’état.
Niger’s Significance on the World Map
Despite the challenges it faces, Niger holds significant importance on the world map for several reasons:
- Strategic Location: Niger’s location in the Sahel region, bordering several countries, makes it strategically important in terms of regional security and stability.
- Natural Resources: Its vast uranium reserves contribute significantly to the global nuclear energy industry.
- Cultural Diversity: Niger’s rich cultural heritage and diverse ethnic groups contribute to the cultural tapestry of Africa.
- International Cooperation: Niger is a recipient of significant international aid and development assistance, highlighting its importance in global efforts to combat poverty and improve living standards.
FAQs
Q: What is the official language of Niger?
A: The official language of Niger is French, a legacy of its colonial past. However, numerous indigenous languages are spoken throughout the country, including Hausa, Zarma, Tuareg, and Kanuri.
Q: What is the currency of Niger?
A: The currency of Niger is the West African CFA franc (XOF).
Q: What are the main tourist attractions in Niger?
A: Niger offers a unique blend of cultural and natural attractions, including:
- Aïr Mountains: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Aïr Mountains are a popular destination for trekking and hiking.
- Ténéré Desert: Known as the "sea of sand," the Ténéré Desert is a vast and desolate landscape, offering a unique glimpse into the Sahara’s harsh beauty.
- National Parks: Niger has several national parks, including the W National Park, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, and the Koure National Park, home to a large population of endangered African wild dogs.
- Traditional Villages: Visiting traditional villages in Niger provides a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of the country.
Tips for Visiting Niger:
- Obtain a visa: Most visitors require a visa to enter Niger.
- Plan your itinerary: Niger is a vast country, so it’s essential to plan your itinerary carefully, considering the distances between destinations and transportation options.
- Respect local customs: Dress modestly and be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Be prepared for harsh conditions: Niger is a challenging country to travel in, with extreme temperatures, limited infrastructure, and potential security risks.
- Hire a guide: Hiring a local guide can enhance your travel experience, providing valuable insights and assistance.
Conclusion
Niger, a nation at the crossroads of cultures and challenges, occupies a vital position on the world map. Despite the economic and social difficulties it faces, its rich history, cultural diversity, and strategic location make it a country of immense significance. By understanding the unique complexities of Niger, we can better appreciate its contributions to the African continent and the global community.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Niger: A West African Nation at the Crossroads of Cultures and Challenges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply