The Red River: A Lifeline Through History And Geography
The Red River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Related Articles: The Red River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Red River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Red River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
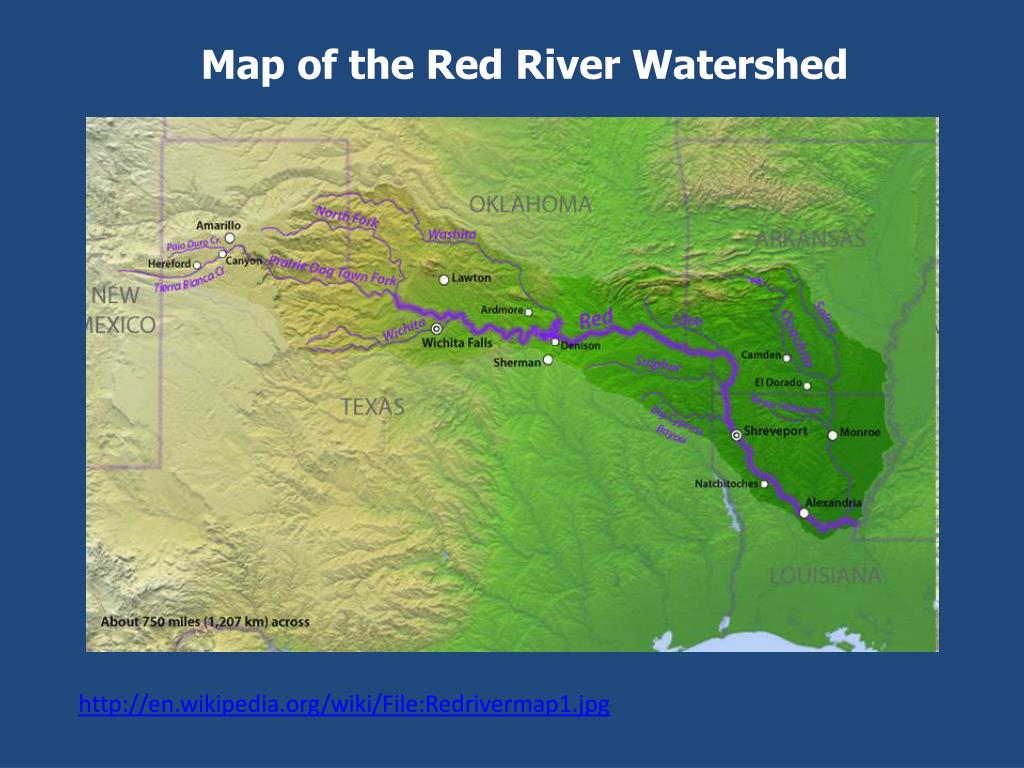
The Red River, a significant waterway in the United States, traverses a vast expanse of land, shaping the landscape and influencing the lives of countless people. Its course meanders through several states, carving a path through history and geography, leaving an indelible mark on the American narrative.
A River of Many Names
The Red River, known by various names throughout its course, holds a rich history steeped in Native American traditions and European exploration. Its Indigenous name, "Sioux" or "Red River of the North," reflects its significance to the indigenous peoples who inhabited the region for centuries. The river’s current name, "Red River," is attributed to the reddish hue of its waters, caused by the erosion of red clay soils along its banks.
The Source and the Journey
The Red River originates in the rolling hills of Otter Tail County, Minnesota, and flows southward for over 1,200 miles, eventually emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. Its journey takes it through the heart of the Great Plains, traversing diverse landscapes, including prairies, forests, and swamps. As the river winds its way through the states of Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota, Oklahoma, and Texas, it serves as a vital lifeline for communities, providing water for agriculture, industry, and recreation.
Historical Significance
The Red River has played a pivotal role in the history of the United States. It was a vital trade route for Native Americans, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. European explorers and fur traders, recognizing the river’s strategic importance, followed its course, establishing trading posts and settlements along its banks. The Red River played a crucial role in the westward expansion of the United States, serving as a pathway for pioneers, settlers, and merchants.
The Red River Valley: A Land of Abundance
The Red River Valley, a fertile expanse of land along the river’s course, has long been recognized for its agricultural bounty. The rich soil, abundant water supply, and temperate climate have made the valley a major agricultural producer, contributing significantly to the nation’s food supply. The valley’s agricultural heritage is evident in the vast fields of wheat, corn, and other crops that stretch across its landscape.
Navigational Challenges and Importance
While the Red River has historically served as a vital waterway, its navigability has been subject to challenges. The river’s flow fluctuates significantly, making it prone to droughts and floods, impacting navigation. Despite these challenges, the Red River continues to be a significant transportation route for goods and people, particularly in the northern part of its course.
The Red River Today
Today, the Red River continues to play a vital role in the lives of communities along its banks. It provides water for agriculture, industry, and recreation, while also supporting a diverse ecosystem of flora and fauna. The river’s beauty attracts visitors from across the country, who come to enjoy its natural wonders and engage in activities such as fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing.
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
Despite its importance, the Red River faces a number of environmental challenges. Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban development has impacted water quality and threatened the health of the river’s ecosystem. To address these concerns, various conservation efforts are underway, focusing on reducing pollution, restoring habitats, and promoting sustainable practices.
The Red River: A Legacy of Resilience and Adaptation
The Red River’s history is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the human spirit. From its role in Native American culture to its significance in the westward expansion of the United States, the river has witnessed countless transformations and challenges. Today, the Red River continues to be a vital resource for communities and a symbol of the enduring connection between humans and the natural world.
FAQs about the Red River
Q: What are the major cities located along the Red River?
A: Major cities located along the Red River include Fargo, North Dakota; Grand Forks, North Dakota; Winnipeg, Manitoba; and Shreveport, Louisiana.
Q: What are the main tributaries of the Red River?
A: Some of the major tributaries of the Red River include the Bois de Sioux River, the Sheyenne River, the Pembina River, the Red Lake River, and the Washita River.
Q: What are the key industries in the Red River Valley?
A: Key industries in the Red River Valley include agriculture, manufacturing, energy production, and tourism.
Q: What are the major environmental concerns affecting the Red River?
A: Major environmental concerns affecting the Red River include agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, urban development, and habitat loss.
Q: What are some of the conservation efforts being undertaken to protect the Red River?
A: Conservation efforts to protect the Red River include reducing agricultural runoff, promoting sustainable farming practices, restoring degraded habitats, and educating the public about the importance of water conservation.
Tips for Visiting the Red River
1. Explore the Red River Valley: Embark on a scenic drive through the Red River Valley, stopping at historic sites, farms, and towns along the way.
2. Visit the Red River National Wildlife Refuge: Discover the diverse wildlife and habitats of the Red River National Wildlife Refuge, home to a variety of birds, mammals, and reptiles.
3. Explore the Red River Museum: Learn about the history, culture, and environment of the Red River at the Red River Museum, located in Fargo, North Dakota.
4. Enjoy outdoor recreation: Engage in activities such as fishing, boating, kayaking, and hiking along the Red River and its tributaries.
5. Attend local festivals and events: Experience the vibrant culture of the Red River Valley by attending local festivals and events, such as the Red River Valley Fair and the Fargo Marathon.
Conclusion
The Red River, a lifeline through history and geography, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of nature, culture, and human activity. Its course has shaped the landscape, influenced the lives of countless people, and left an enduring mark on the American narrative. As we continue to navigate the challenges of the 21st century, the Red River serves as a reminder of the importance of preserving our natural resources, respecting our shared history, and fostering a sustainable future for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Red River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply