Unraveling The Network: A Comprehensive Guide To The Peripheral Nervous System Map
Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System Map

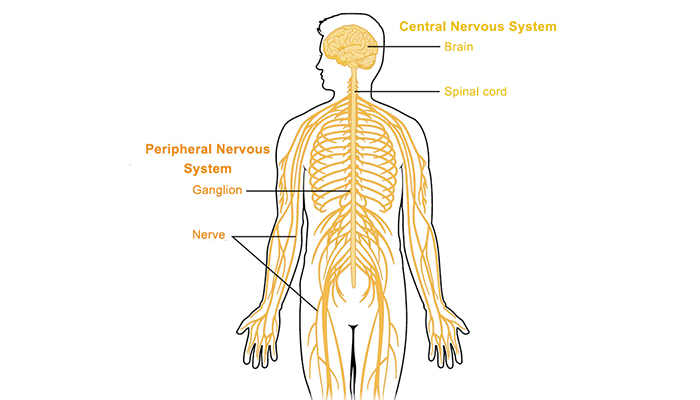
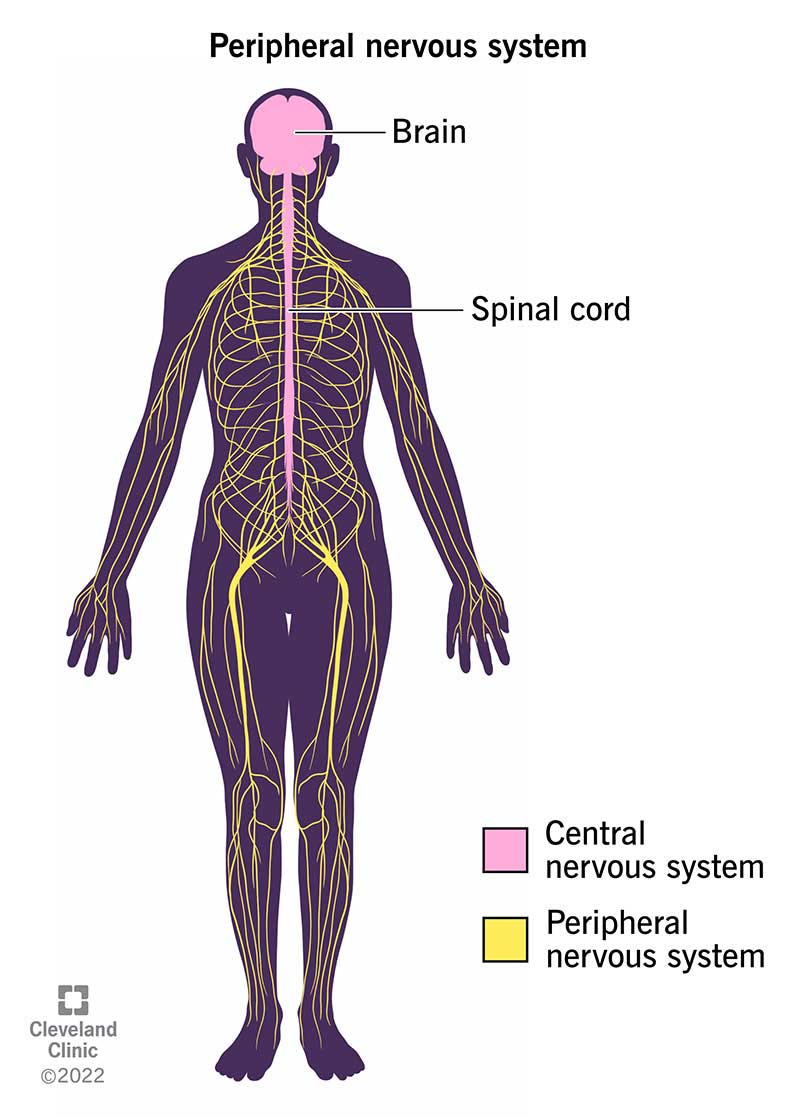
The human body is a marvel of intricate systems working in concert. One such system, the nervous system, serves as the body’s control center, orchestrating everything from our simplest reflexes to our most complex thoughts. While the central nervous system (CNS), comprised of the brain and spinal cord, takes the spotlight, the peripheral nervous system (PNS) plays a crucial role in connecting the CNS to the rest of the body.
Understanding the Peripheral Nervous System
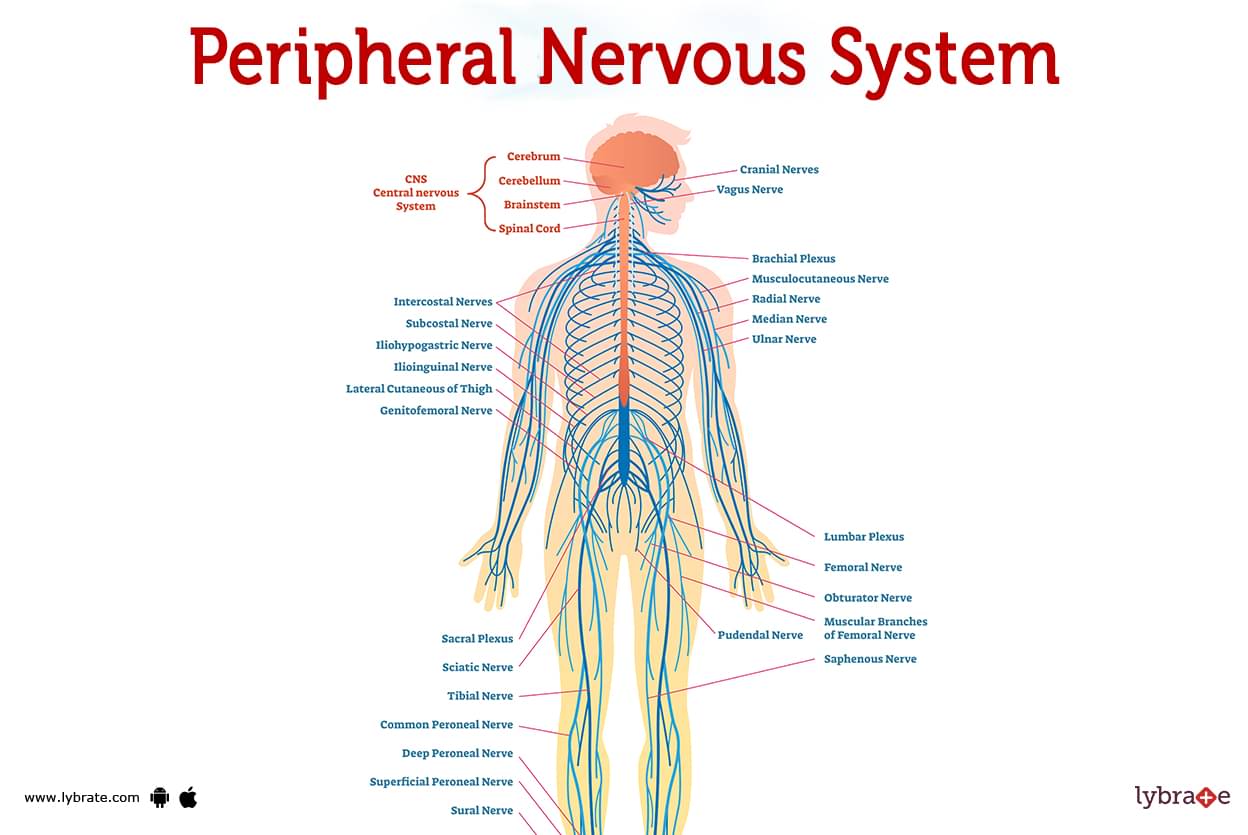
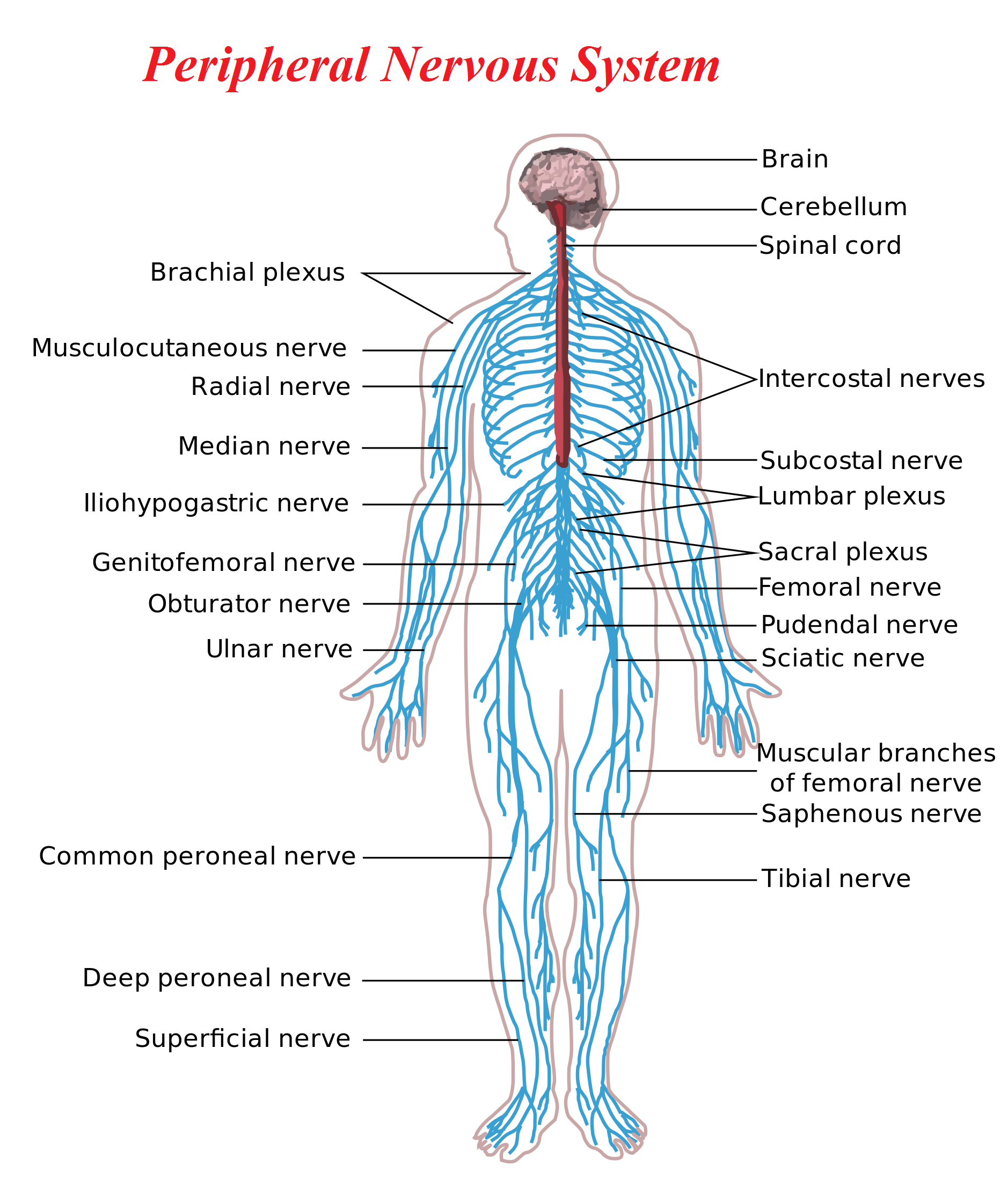
The PNS acts as the communication highway, transmitting signals between the CNS and the body’s organs, muscles, and glands. It comprises a vast network of nerves that extend outward from the spinal cord, branching throughout the body like a delicate web.
The Significance of the Peripheral Nerve Map
A peripheral nerve map, often referred to as a "nerve chart," is a visual representation of the PNS, illustrating the anatomical pathways of individual nerves. These maps are invaluable tools for healthcare professionals, providing a comprehensive understanding of the intricate connections within the PNS.
Dissecting the Peripheral Nerve Map: Key Components
A peripheral nerve map typically depicts the following key components:
- Cranial Nerves: These twelve pairs of nerves originate directly from the brain, controlling functions such as sight, hearing, taste, smell, and facial movements.
- Spinal Nerves: These nerves emerge from the spinal cord, branching out to innervate the limbs, trunk, and organs.
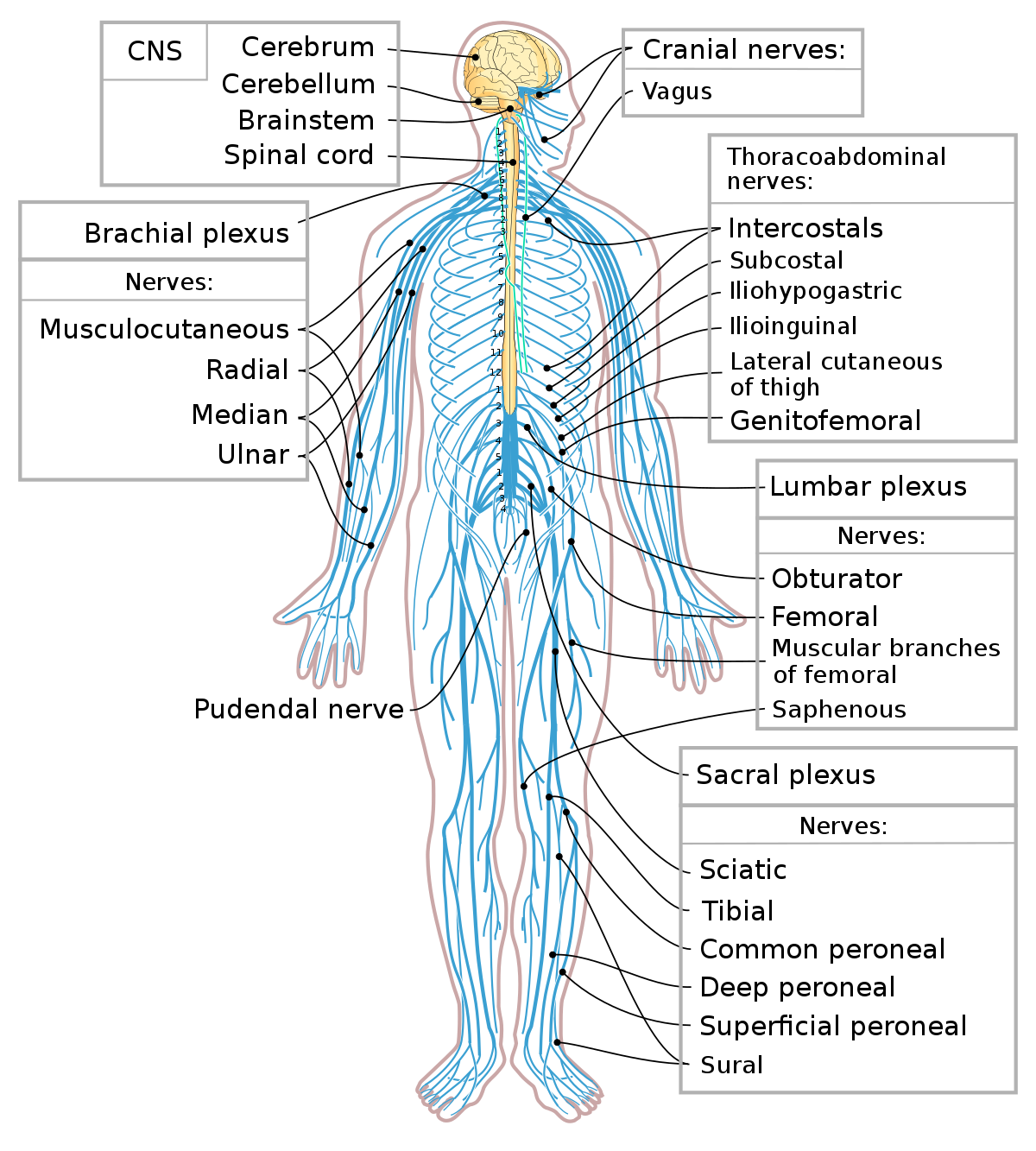
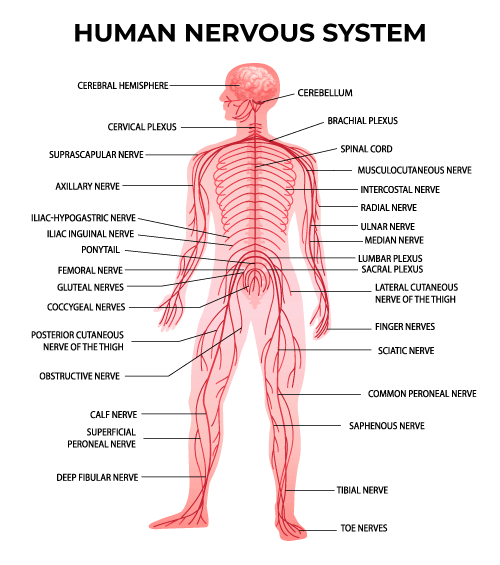
- Plexuses: These are complex networks of nerves formed by the intertwining of spinal nerves. The major plexuses include the cervical plexus (neck), brachial plexus (shoulder and arm), lumbar plexus (lower back and leg), and sacral plexus (pelvis and leg).
- Peripheral Nerves: These are individual nerves that branch out from the plexuses and travel to specific regions of the body, carrying sensory information and motor commands.
Benefits of the Peripheral Nerve Map
The peripheral nerve map serves as a critical resource in various medical disciplines, offering numerous benefits:
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Disorders: By mapping the distribution of nerves, healthcare professionals can pinpoint the location of nerve damage or dysfunction, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, and sciatica.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgeons rely on nerve maps to identify and avoid crucial nerves during surgeries, minimizing the risk of complications.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Understanding nerve pathways helps therapists design targeted treatments for nerve injuries and disorders, promoting optimal recovery and function.
- Pain Management: Identifying the affected nerve can guide pain management strategies, leading to more effective and targeted pain relief.
- Medical Education: Nerve maps are indispensable tools for medical students and professionals, providing a visual understanding of the complex anatomy and function of the PNS.
Navigating the Peripheral Nerve Map: A Closer Look
To understand the peripheral nerve map more effectively, it is helpful to explore specific examples:
- The Brachial Plexus: This network of nerves controls the shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand. It is often affected in injuries involving the neck or shoulder, leading to weakness, numbness, and pain in the upper limb.
- The Sciatic Nerve: This longest nerve in the body originates from the sacral plexus and travels down the leg, supplying sensation and motor control to the leg and foot. Sciatica, a condition characterized by pain radiating down the leg, is caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve.
- The Facial Nerve: This cranial nerve controls facial expressions, taste sensation on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and tear production. Damage to the facial nerve can lead to facial paralysis (Bell’s palsy) or loss of taste sensation.
FAQs Regarding the Peripheral Nerve Map
1. How does the peripheral nerve map help diagnose nerve damage?
By examining the distribution of nerve pathways, healthcare professionals can identify areas of sensory loss, muscle weakness, or pain, which can indicate nerve damage.
2. Can the peripheral nerve map be used to predict potential nerve injury during surgery?
Yes, surgeons use nerve maps to visualize the location of nerves and avoid injuring them during surgical procedures.
3. What are some common conditions that affect the peripheral nervous system?
Common conditions affecting the PNS include neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, sciatica, Bell’s palsy, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
4. Can the peripheral nerve map be used to guide physical therapy treatment?
Yes, understanding nerve pathways helps therapists design targeted exercises and treatments to promote nerve regeneration and restore function.
5. Are there any limitations to using the peripheral nerve map?
While nerve maps are invaluable tools, they are simplified representations of complex anatomical structures. Individual variations in nerve anatomy can exist, and the maps may not always perfectly reflect the specific nerve pathways in each individual.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the Peripheral Nerve Map
- Visualize the Connections: Imagine the nerve pathways as interconnected highways, transporting signals throughout the body.
- Focus on Key Landmarks: Memorize the major nerve plexuses and their branches to better understand the nerve distribution in different regions.
- Relate to Clinical Applications: Think about how the nerve map can be used to diagnose and treat specific conditions.
- Utilize Online Resources: Explore interactive nerve maps and online resources to enhance your understanding.
Conclusion: The Peripheral Nerve Map – A Vital Tool for Understanding the Body’s Communication Network
The peripheral nerve map serves as a crucial bridge between the central nervous system and the body’s periphery. By understanding the intricate connections within the PNS, healthcare professionals can diagnose and treat neurological disorders, guide surgical procedures, optimize physical therapy, and improve pain management. As a vital tool in medical education and practice, the peripheral nerve map continues to play an indispensable role in advancing our knowledge of the body’s intricate communication network.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peripheral Nervous System Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply