Unveiling The Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps

Snow, a ubiquitous element of winter landscapes, holds a significant role in shaping ecosystems, influencing human activities, and impacting weather patterns. Understanding the distribution and depth of snow across the globe is crucial for diverse sectors, from agriculture and transportation to water resource management and disaster preparedness. Current snow depth maps, generated using a combination of satellite imagery, ground-based observations, and sophisticated modeling techniques, provide an invaluable snapshot of this dynamic element of the Earth’s surface.
Deciphering the Data: Interpreting Current Snow Depth Maps
Current snow depth maps, often displayed as colorful visualizations, depict the depth of snow cover across a specific geographical area. The maps utilize color gradients or numerical scales to represent varying snow depths, allowing users to quickly identify areas with deep snow accumulations, moderate snow cover, or minimal snowfall.
The Power of Observation: Data Sources for Snow Depth Mapping
Creating accurate and up-to-date snow depth maps relies on a multi-faceted approach, incorporating data from various sources:
-
Satellite Remote Sensing: Satellites equipped with specialized sensors, such as microwave radiometers, can penetrate cloud cover and measure snow depth by analyzing the emitted microwave radiation. This technique is particularly useful for vast and remote areas, providing a global perspective on snow cover.
-
Ground-Based Observations: Snow depth measurements collected from weather stations, ski resorts, and other ground-based locations provide localized and highly accurate data points. These observations act as ground truth for verifying and calibrating satellite data, ensuring greater map accuracy.
-
Numerical Weather Models: Advanced weather models, incorporating atmospheric conditions and snow accumulation processes, simulate snow depth distribution. These models provide valuable estimates, especially in areas with limited observational data.
The Importance of Snow Depth Maps: Applications Across Diverse Sectors
Snow depth maps serve as valuable tools across various sectors, impacting decision-making processes and informing critical operations:
-
Water Resource Management: Snowmelt provides a significant portion of water supply for many regions. Snow depth maps help water resource managers assess the potential water yield from snowpack, enabling them to anticipate water availability and plan for potential shortages.
-
Agriculture: Snow cover acts as a natural insulator, protecting crops and livestock from extreme winter temperatures. Farmers can use snow depth maps to monitor the extent of snow cover and plan for potential frost damage, optimizing agricultural practices.
-
Transportation: Snowfall can significantly disrupt transportation systems, leading to road closures and flight delays. Snow depth maps enable transportation authorities to anticipate potential hazards, prioritize snow removal efforts, and ensure safer travel conditions.
-
Disaster Preparedness: Heavy snowfall can trigger avalanches and other natural hazards. Snow depth maps help disaster management agencies identify areas at risk, plan for potential evacuations, and allocate resources effectively.
-
Climate Monitoring and Research: Snow depth maps provide crucial data for climate monitoring and research, enabling scientists to track changes in snow cover over time, understand the impact of climate change, and predict future trends.
Understanding the Limitations: Considerations for Using Snow Depth Maps
While snow depth maps offer valuable insights, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations:
-
Spatial Resolution: The accuracy of snow depth maps can vary depending on the data source and the spatial resolution of the data. Satellite data may have coarser resolution than ground-based observations, potentially leading to inaccuracies in areas with complex terrain or localized snow accumulation patterns.
-
Temporal Resolution: Snow depth maps are snapshots in time, reflecting conditions at a specific point. The rapidly changing nature of snow cover, influenced by snowfall, melting, and wind redistribution, means that maps may not accurately reflect real-time conditions.
-
Data Availability: Data availability can vary geographically, with some areas having more extensive ground-based observations and satellite coverage than others. This can result in gaps in information and potentially reduced map accuracy in certain regions.
FAQs about Current Snow Depth Maps
Q: How often are snow depth maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the specific data source and the mapping process. Some maps are updated daily, while others may be updated weekly or monthly.
Q: What is the accuracy of snow depth maps?
A: The accuracy of snow depth maps varies depending on the data source, spatial resolution, and the terrain. Satellite data generally has lower accuracy than ground-based observations.
Q: How can I access current snow depth maps?
A: Many government agencies, research institutions, and private companies provide access to current snow depth maps through their websites, online portals, and mobile applications.
Q: What are the applications of snow depth maps in climate change research?
A: Snow depth maps play a critical role in climate change research by providing data on long-term trends in snow cover, enabling scientists to assess the impact of climate change on snow accumulation, melt patterns, and water availability.
Tips for Using Current Snow Depth Maps Effectively
-
Consider the data source: Pay attention to the data source and the mapping method used to understand the potential limitations of the map.
-
Check the date and time: Remember that snow depth maps are snapshots in time, and snow conditions can change rapidly.
-
Use multiple sources: Compare data from different sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of snow depth distribution.
-
Consult with experts: For specific applications or complex analyses, consult with experts in snow hydrology, meteorology, or related fields.
Conclusion
Current snow depth maps provide invaluable insights into the distribution and depth of snow cover, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. By understanding the data sources, limitations, and applications of these maps, individuals and organizations can harness their power to optimize resource management, enhance transportation safety, mitigate natural hazards, and advance climate change research. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect increasingly sophisticated and accurate snow depth maps, further enhancing our understanding of this vital component of the Earth’s cryosphere.
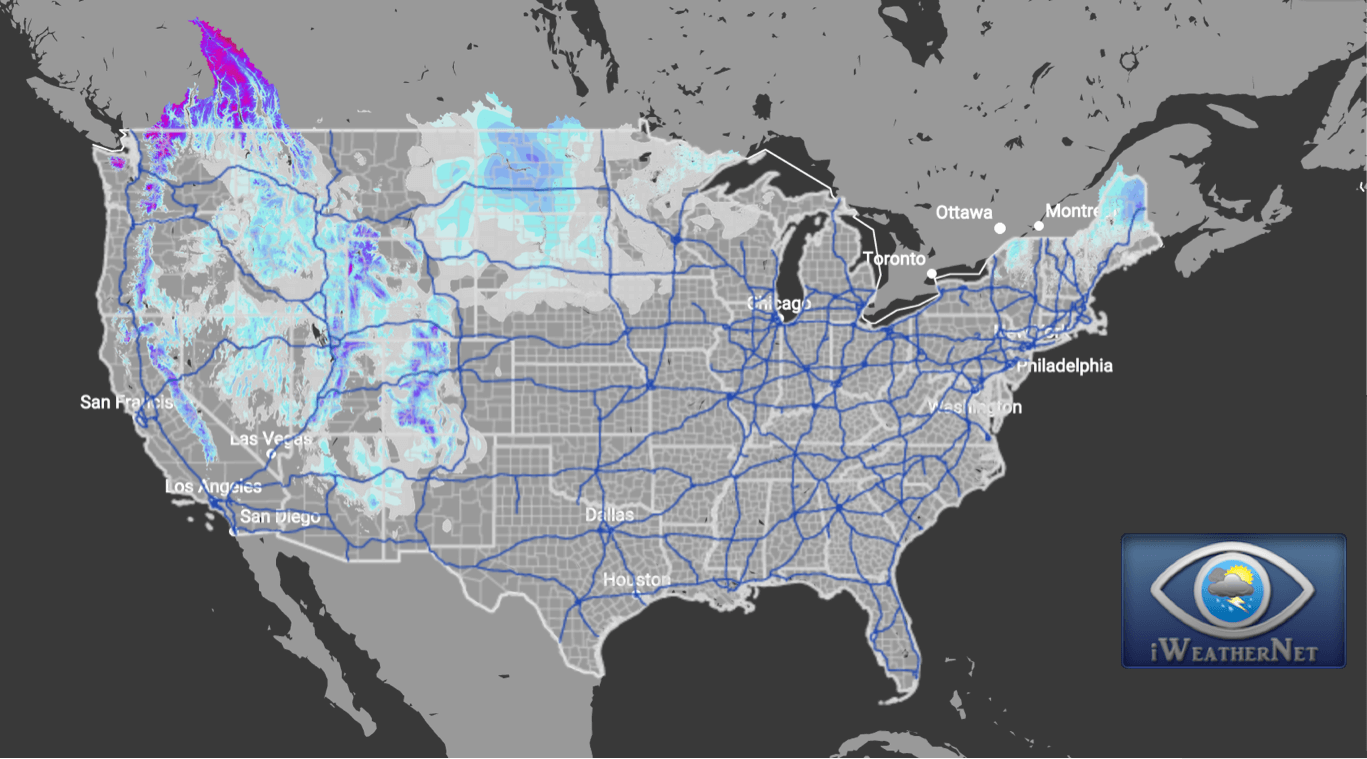
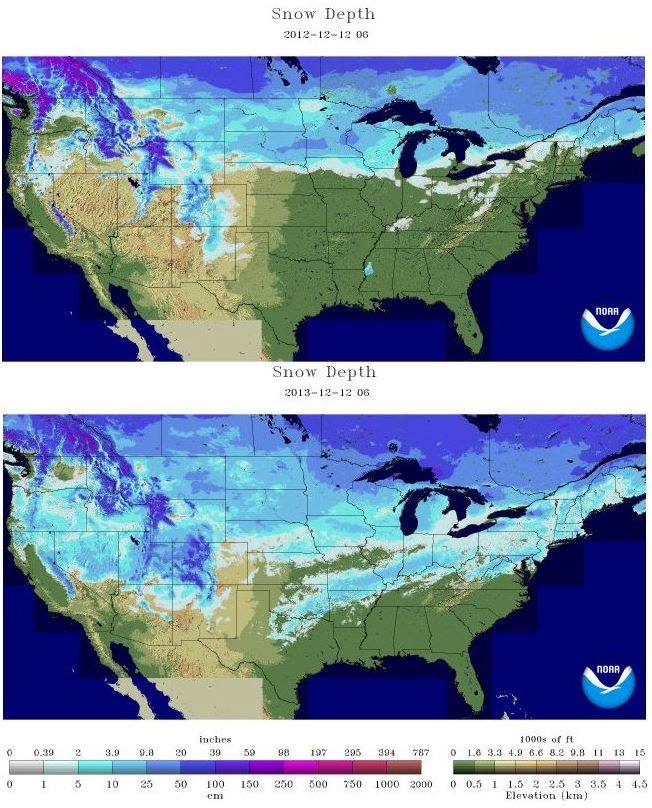




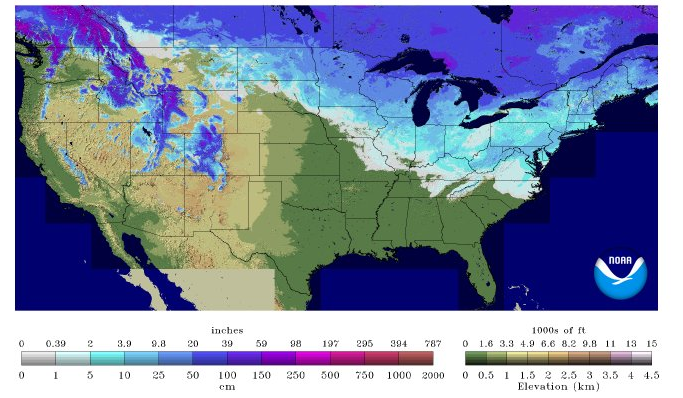
/https://blogs-images.forbes.com/dennismersereau/files/2019/03/2018-2019-snow-1200x784.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Depth Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Wild: Understanding Wyoming’s Hunting Unit Map
- 511.org Map
- Navigating Nevada’s Smoke: Understanding And Utilizing Smoke Maps
- Understanding The Sheikh Jarrah Map: A Historical And Geopolitical Analysis
- Navigating Safety: Understanding Oregon’s Fire Evacuation Maps
- Navigating Chicago: A Comprehensive Guide To The CTA Orange Line
- Navigating The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Ireland’s Airports
- Navigating Denver’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a Reply